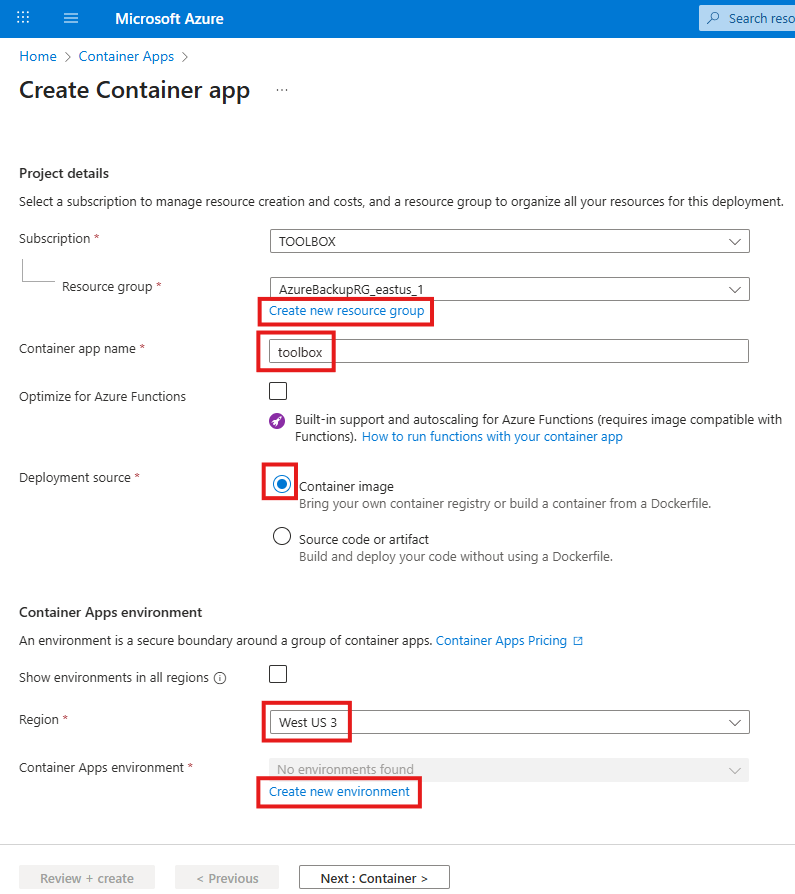
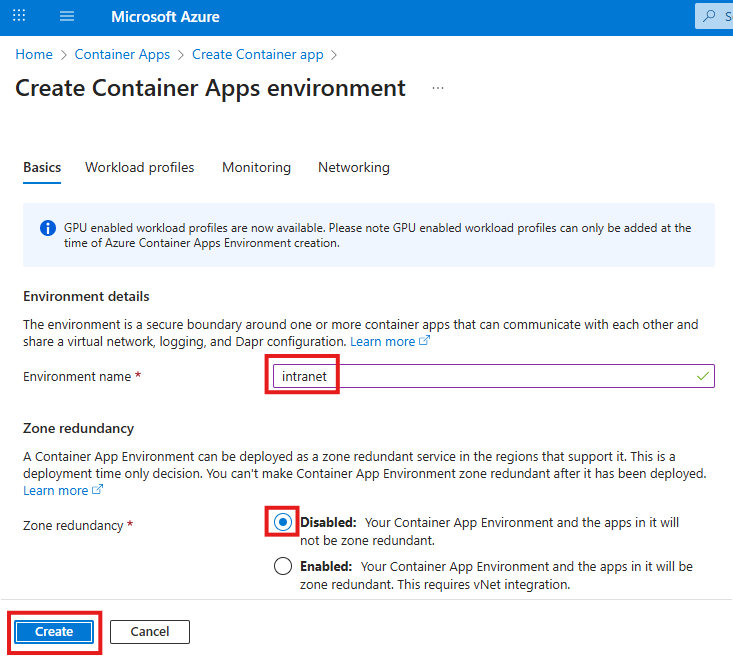
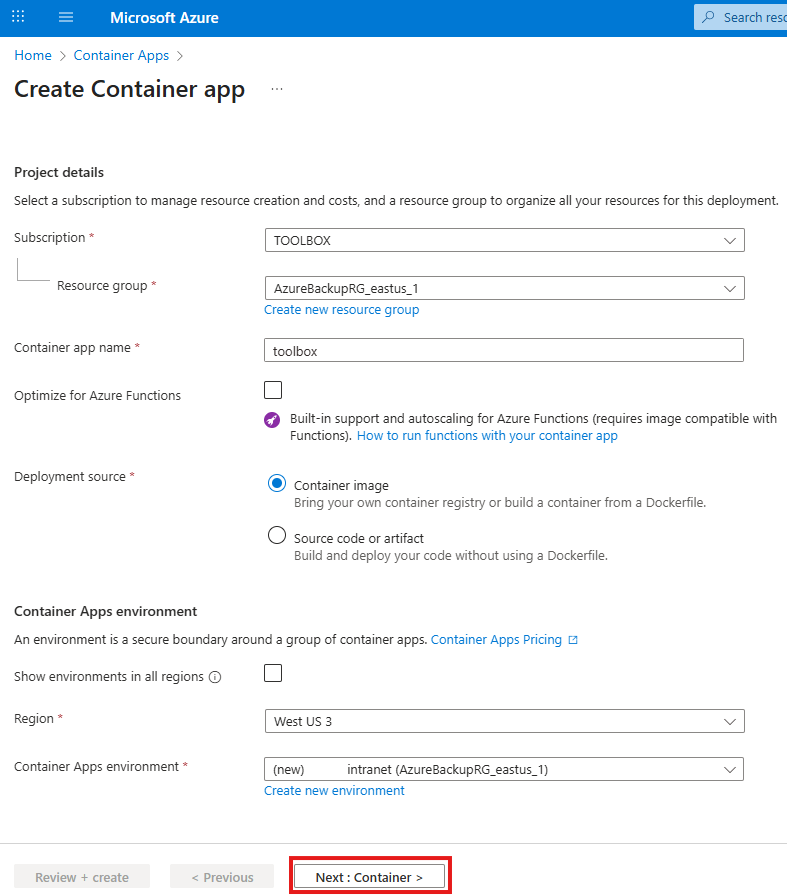
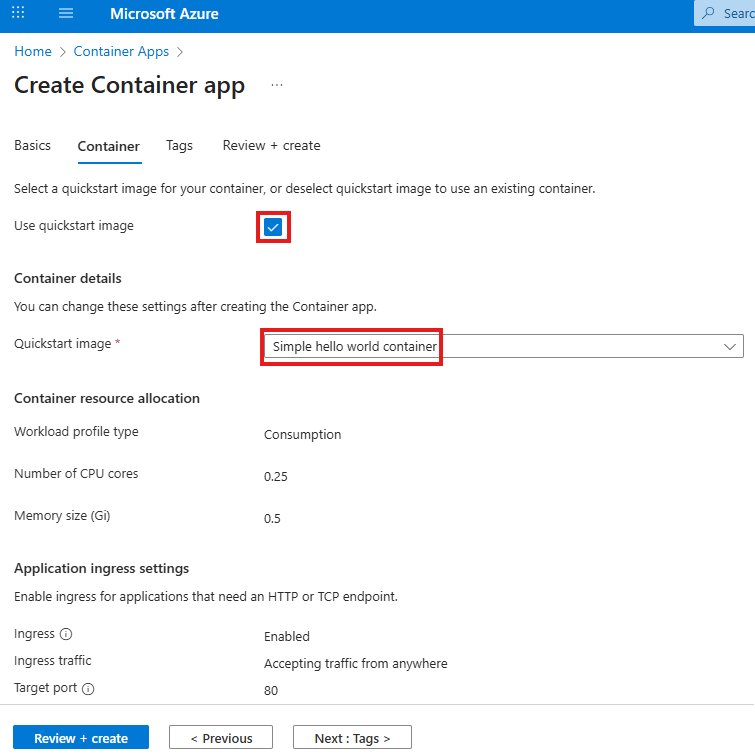
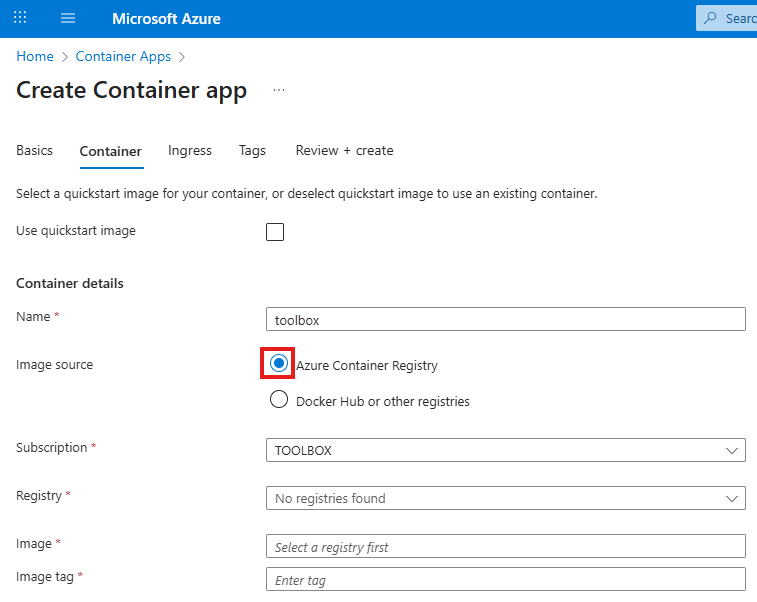
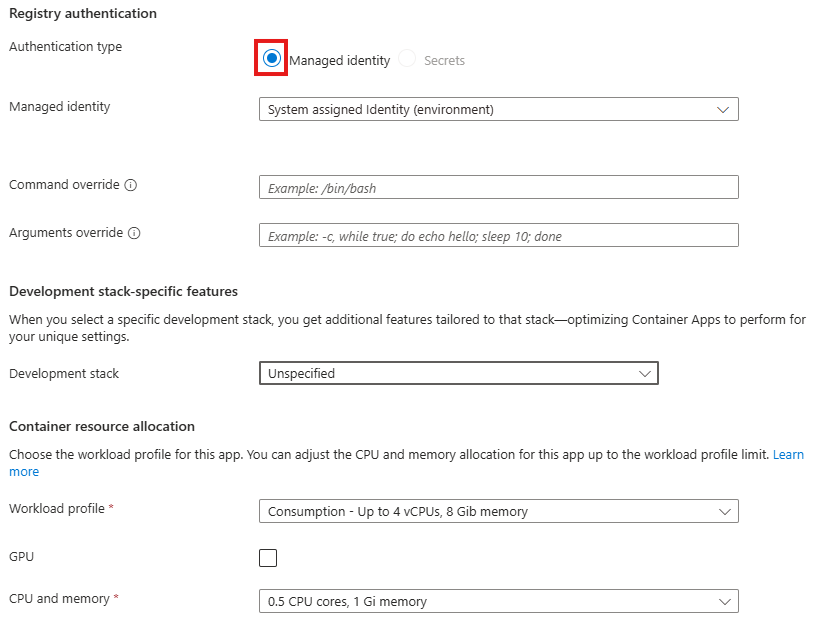
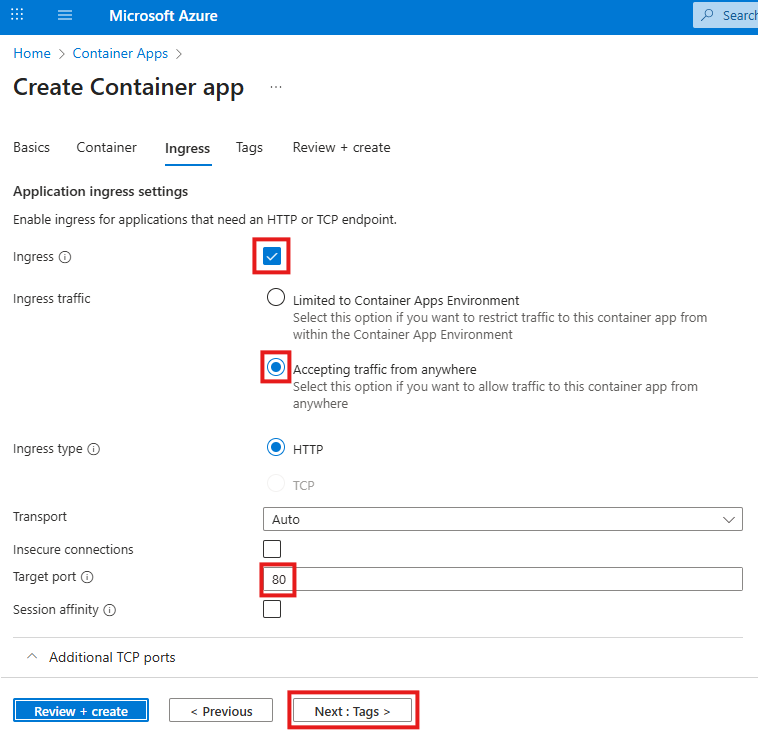
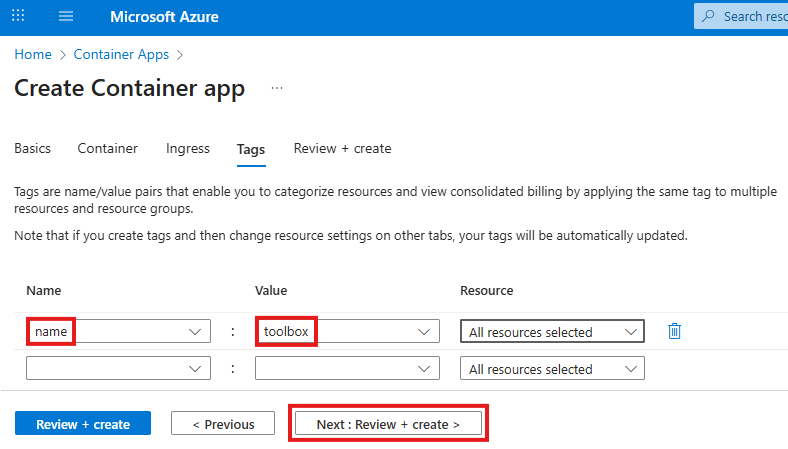
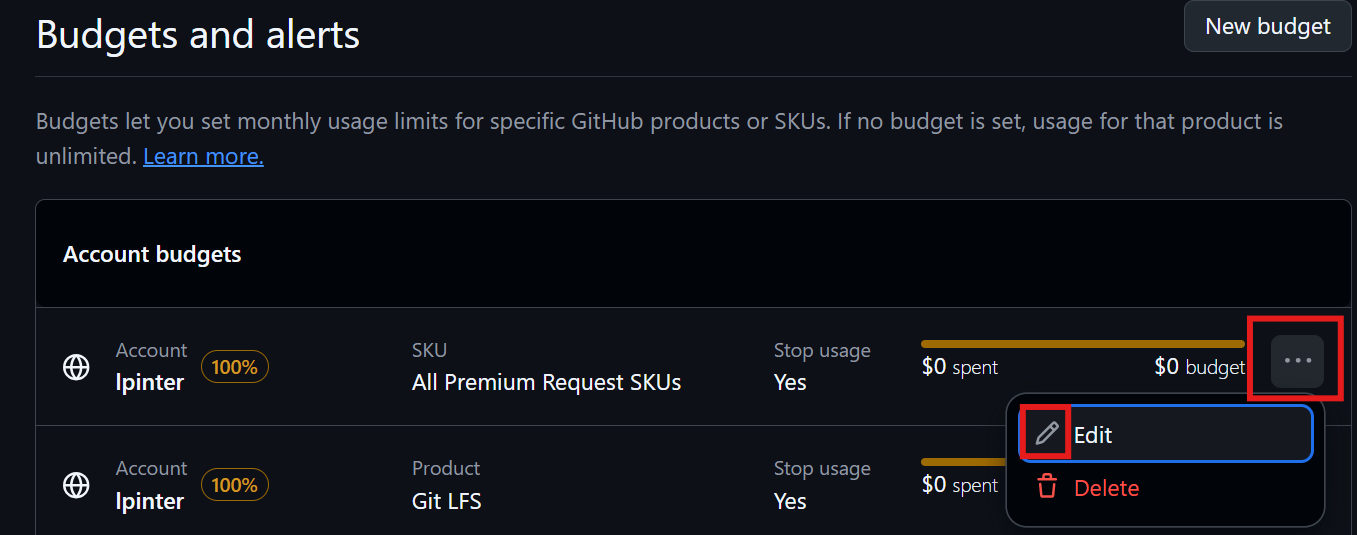
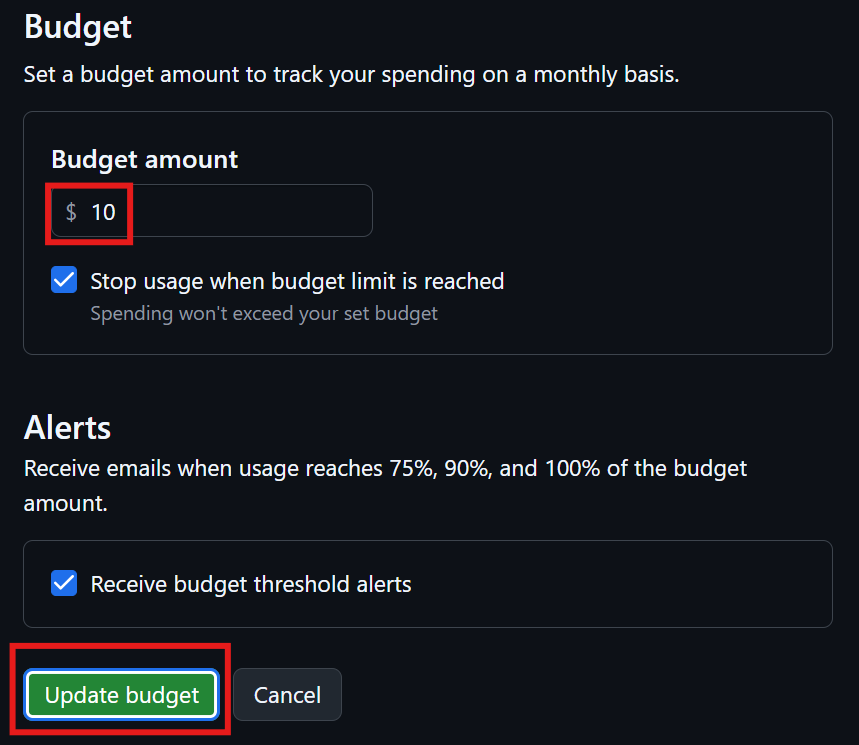
You may apply these configuration settings to enable useful features. Always read the documentation to see if these are safe and beneficial to you.
Copilot Memory
You can use Copilot Memory to remember repository context across Copilot agent interactions.
- On the https://github.com/settings/copilot/features page enable Copilot Memory
To store a memory start the prompt with “Remember: …”
More information on GitHub Copilot memories are at https://docs.github.com/en/copilot/how-tos/use-copilot-agents/copilot-memory
Checkpoint file changes
chat.checkpoints.showFileChanges set to ON
Explain button
chat.editing.explainChanges.enabled set to ON
Inline Chat Enable V2
If you want to experiment with the new inline chat feature enable
inlineChat.enableV2
Usage suggestions
Hide Sessions
When the chat window is wide enough it displays the list of prior sessions. It is useful, but prevents us to widen the chat window for better reading experience. We can disable this behavior using the chat.viewSessions.enabled setting, or close the prior sessions with the Hide Agent Sessions Sidebar button