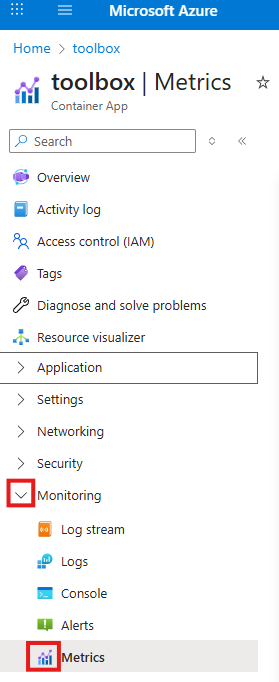
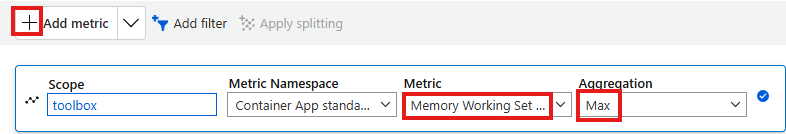
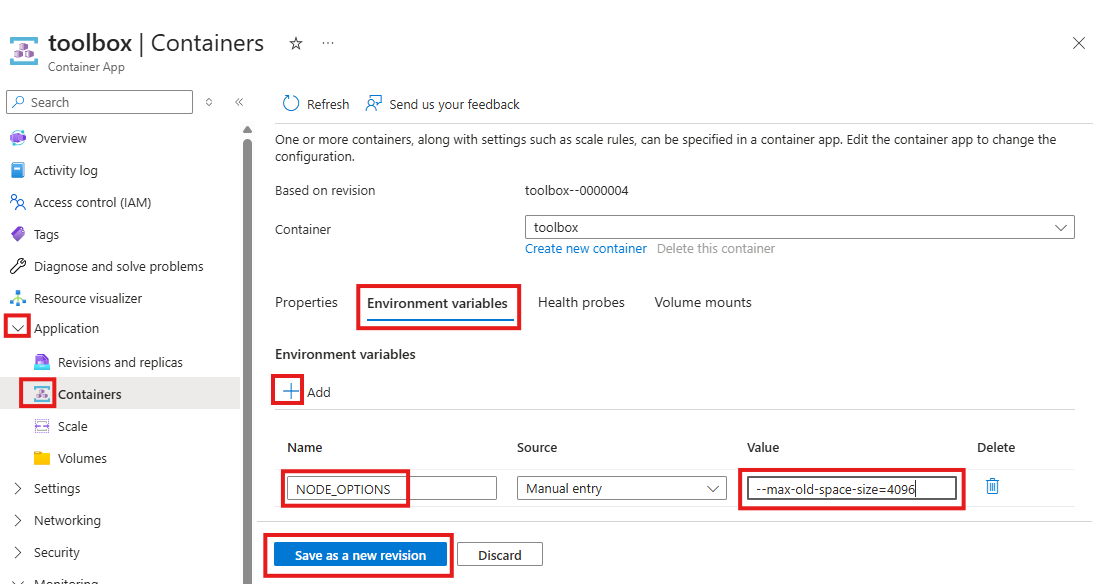
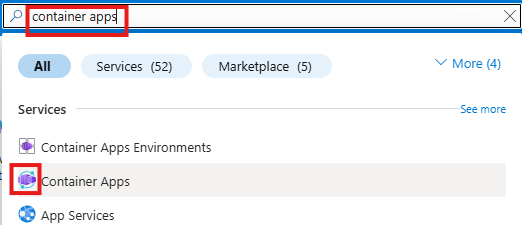
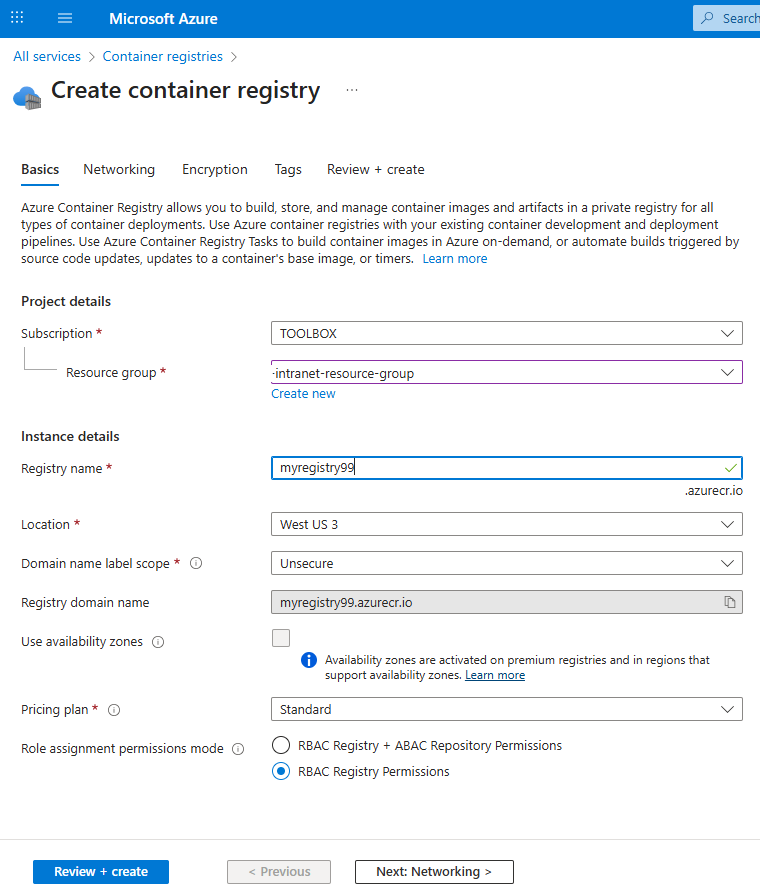
Material UI is a great Google React UI component library. It looks great, provides consistent look for web applications, but it has two disadvantages:
- The icon library has more than 9000 icons, it takes a long time to load all of them, as there is no tree shaking to ignore the unused items.
- The Tailwind styling classes don’t always work, because the Material UI built-in themes of colors and other settings take precedent.
Material Tailwind is an opensource library recreating the consistent look of Material UI, but allowing Tailwind themes to control the look.
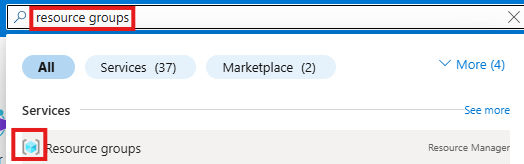
To set a React Router (Remix) web application to use Material Tailwind
Install Tailwind CSS with React Router (Remix)
Install Tailwind CSS
pnpm install tailwindcss @tailwindcss/vite
Configure the Vite plugin. Add the bold lines to the vite.config.js file
import { reactRouter } from "@react-router/dev/vite";
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import tsconfigPaths from "vite-tsconfig-paths";
import tailwindcss from "@tailwindcss/vite";
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
tailwindcss(),
reactRouter(),
tsconfigPaths(),
],
});
Add to the app.css file
@import "tailwindcss";
See Install Tailwind CSS with React Router
Install @material-tailwind/react as a dependency
Execute the command
pnpm i @material-tailwind/react
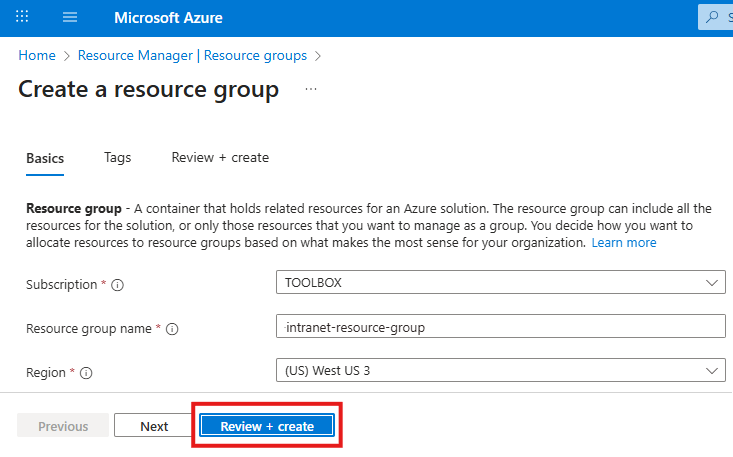
Create the tailwind.config.js file in the root of the web application directory
const withMT = require("@material-tailwind/react/utils/withMT");
module.exports = withMT({
content: ["./app/**/*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}"], // Add your template paths here
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
});
If you are using a monorepo, to host multiple applications in the same repository, and the node_modules directory is not in the application directory, use this tailwind.config.js file in the root of the web application
import type { Config } from "tailwindcss";
import withMT from "@material-tailwind/react/utils/withMT";
export default withMT({
content: [
"./app/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}",
"path-to-your-node_modules/@material-tailwind/react/components/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}",
"path-to-your-node_modules/@material-tailwind/react/theme/components/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}",
],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
} satisfies Config);
Theme Provider
Wrap the entire application with the ThemeProvider. Create the app/entry.client file
import { RemixBrowser } from "@remix-run/react";
import { startTransition } from "react";
import { hydrateRoot } from "react-dom/client";
import { ThemeProvider } from "@material-tailwind/react";
startTransition(() => {
hydrateRoot(
document,
<ThemeProvider>
<RemixBrowser />
</ThemeProvider>
);
});
Web page example
This example displays a button using the Material Tailwind library
import MaterialTailwind from "@material-tailwind/react";
const { Button } = MaterialTailwind;
export default function Example() {
return <Button>Button</Button>;
}
See Material Tailwind with Remix