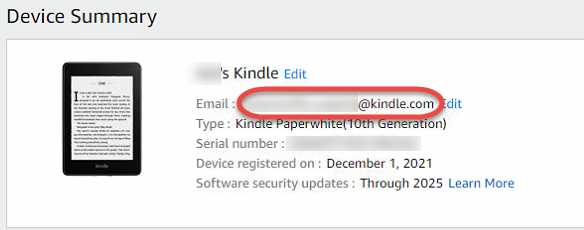
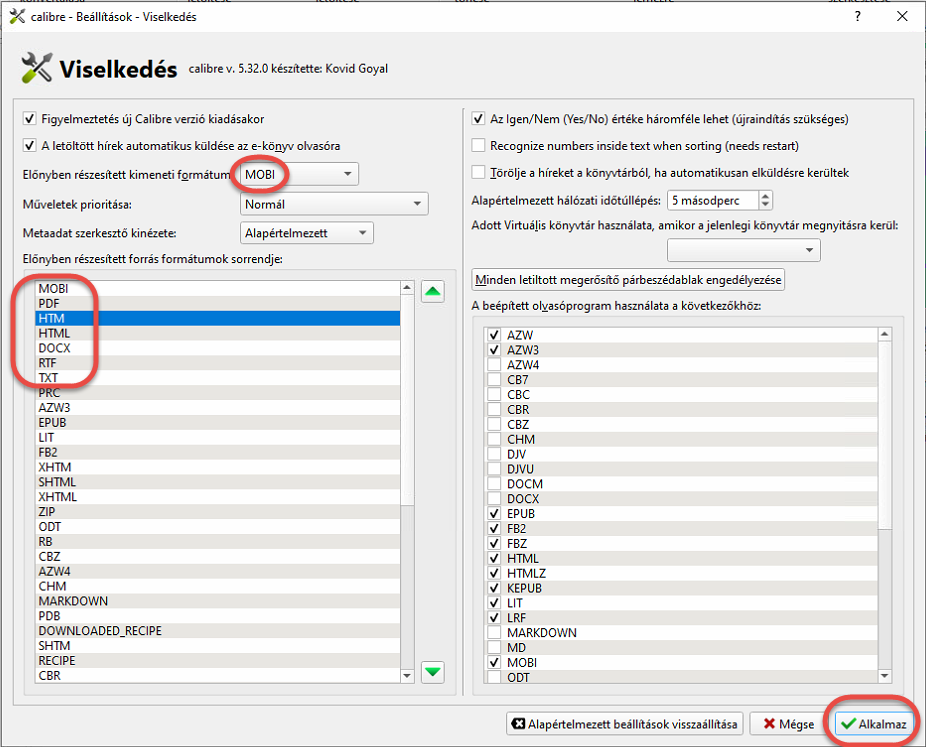
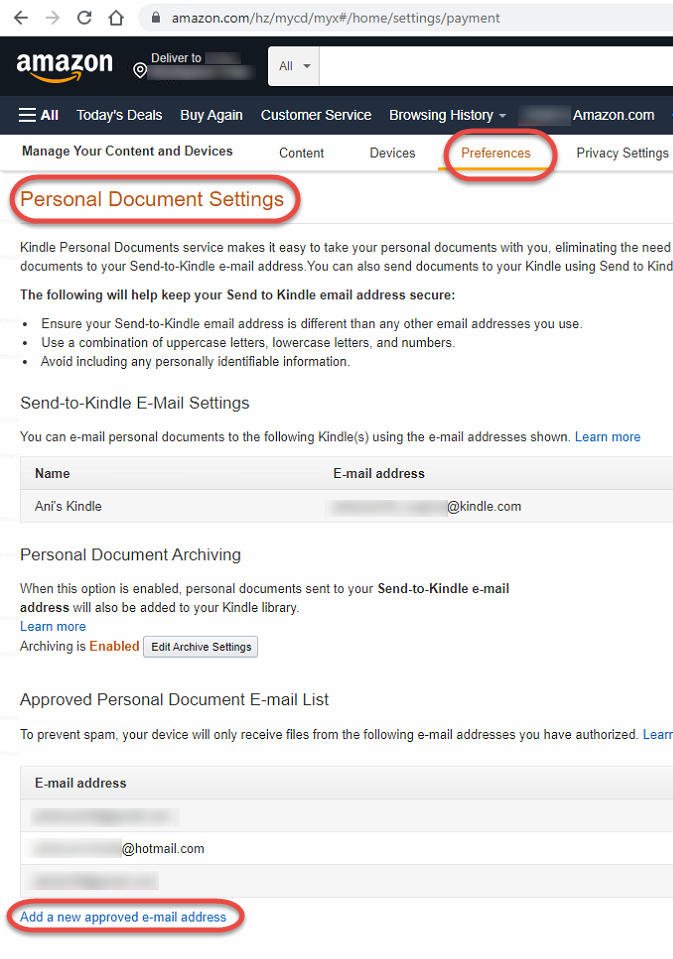
When we start to use a Python module, we need to install it on our workstation, and on the server, or in the Docker container where the application will run.
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘googleapiclient’
Usually, we install the module with the pip install MODULE_NAME command, but when we try it for the googleapiclient we get the error message
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement googleapiclient (from versions: none)
ERROR: No matching distribution found for googleapiclient
To install the googleapiclient Python module, use the command
pip install google-api-python-clientTo install the module in the Docker container add the line to the Dockefile
# Install app dependencies
run pip install --upgrade google-api-python-client