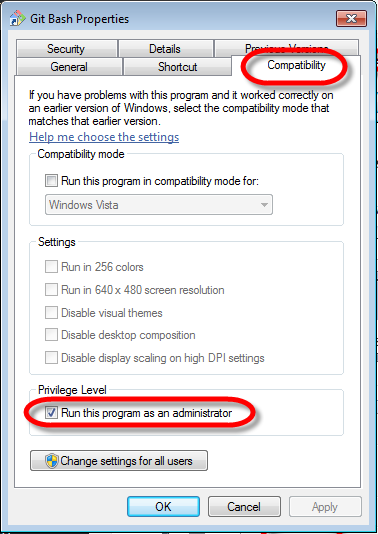
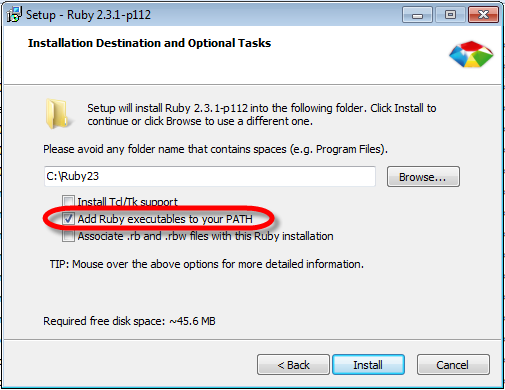
In the first part of the series, Beginner’s Guide to DevOps Engineering Part 1. we have already installed the DevOps development tools.
Create and test your first cookbook in 5 minutes
Set up the Chef working folder
- Create a folder for the Chef development
- on Mac ~/Chef
- on Windows C:\Chef
- In the Chef folder create a sub-folder cookbooks
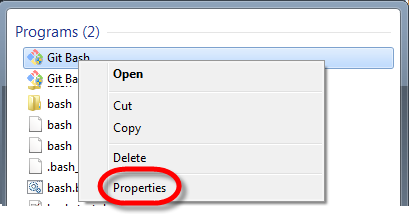
- Right-click the cookbooks folder
- on Mac select Services, iTerm2 in Finder
- on Windows select Git Bash Here
Create your first cookbook
-
- Enter the following command into the Bash window to create a new cookbook
chef generate cookbook test
- Enter the following command into the Bash window to create a new cookbook
Specify the program you want to use to open .rb files
on Mac
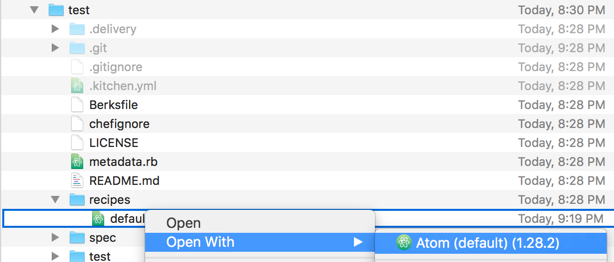
- In Finder navigate to ~/Chef/test/recipes
- Right-click the default.rb file and select Open With, Atom
on Windows
- In File Explorer navigate to the C:\Chef\test\recipes older
- Right-click the default.rb file
- Select Open with
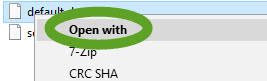
- Select the Always use… checkbox and click the More apps link
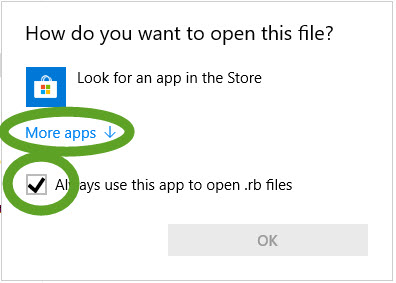
- Select Open with
- Select Notepad++ and click the OK button

Let’s create a file with Hello world in it.
-
-
- Enter the following to create your first recipe
- on Mac
file '/Users/YOUR_USERNAME/Desktop/helloworld.txt' do content 'Hello world' end
- on Windows (make sure you use double backslashes!!!)
file 'C:\\Users\\YOUR_USERNAME\\Desktop\\helloworld.txt' do content 'Hello world' end
- on Mac
- Save the file
- In the bash Window navigate to the test cookbook directory
cd test - Execute your first recipe with the following in the Bash window
chef-client --local-mode recipes/default.rb - Navigate to the Desktop and open the helloworld.txt file to see the result of your script.
- Enter the following to create your first recipe
-
Test your cookbook on a virtual machine
We will use Test Kitchen and Vagrant to launch virtual machines. Currently, only Linux images are available for Vagrant, so we will modify our recipe to select between Linux and Windows and act accordingly.
Open the default.rb recipe and update it to look like this
case node['os']
when 'linux'
file "/tmp/helloworld.txt" do
content 'This file was created by Chef!'
end
when 'windows'
file "C:\\Chef\\helloworld.txt" do
content 'This file was created by Chef!'
end
endEnter the following commands into the Bash window
-
-
- Display the available test configurations ( suites )
kitchen list - Launch a virtual Linux machine and test your recipe
kitchen converge ubuntu
The first time you launch a virtual machine with an operating system you have never used on your workstation, Vagrant has to download the machine image from the Internet. It can take 5-10 minutes. When the virtual machine is created and launched, Test Kitchen will copy your cookbook to it and execute it there. - Test kitchen will display the —–> Kitchen is finished message when the cookbook has successfully executed.
- Log into the virtual machine
kichen login ubuntu - The root prompt appears in the Bash windows. Let’s check if the file has been created or not.
- To destroy the virtual machine
kitchen destroy ubuntu
- Display the available test configurations ( suites )
-
Windows in Vagrant
To test your cookbook on a Windows virtual machine locally, create one for Vagrant. See Launch Windows instances locally with Chef Test Kitchen for the details.
Learn the basics, so you can ask questions
Chef has a steep learning curve. Chef is not just scripting or programming, but you have to understand how Chef works to be able to use it to configure servers. There are many ways to do the same thing and there is not much documentation to recommend the best way. If you search Google, the problems usually have multiple solutions, and many times the “best” answer is selected based on personal preference. To get started, you should familiarize yourself with the tools, because you will use most of them during the development process.
In this guide I will use a Windows computer as a workstation, but all tools work on Mac and Linux computers.
Vagrant
Learn Vagrant to understand how Test Kitchen manages the test servers on your local machine or at AWS. You will not use vagrant directly, but Test Kitchen uses it to launch servers.
-
-
- Tutorial at https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/getting-started/
-
Chef
-
-
- Quick Start instructions at https://docs.chef.io/quick_start.html
- Make sure you understand the two phase Chef execution model. Read about it at https://coderanger.net/two-pass/
- Demystifying Common Idioms in Chef Recipes at https://www.chef.io/blog/2013/09/04/demystifying-common-idioms-in-chef-recipes/
-
Test Kitchen
-
-
- Tutorial at http://kitchen.ci/docs/getting-started/
-
Ruby
-
-
- Just enough Ruby to work with Chef at https://docs.chef.io/ruby.html
-
Terraform
-
-
- Introduction at https://www.terraform.io/intro/index.html
- Terraform syntax at https://www.terraform.io/docs/configuration/syntax.html
-
Next:
Working with AWS in Beginner’s Guide to DevOps Engineering part 3.
Back:
to the Tutorials page