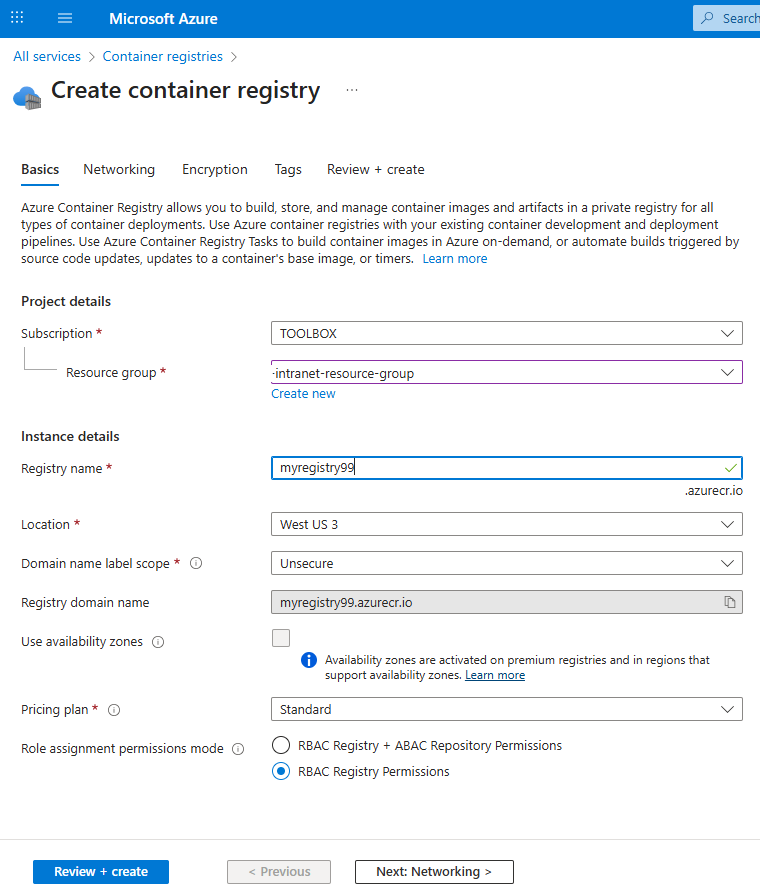
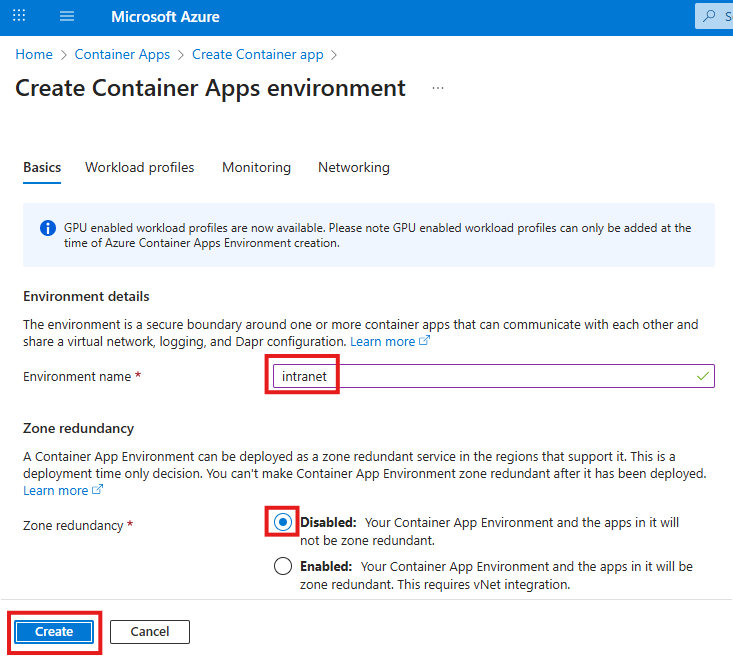
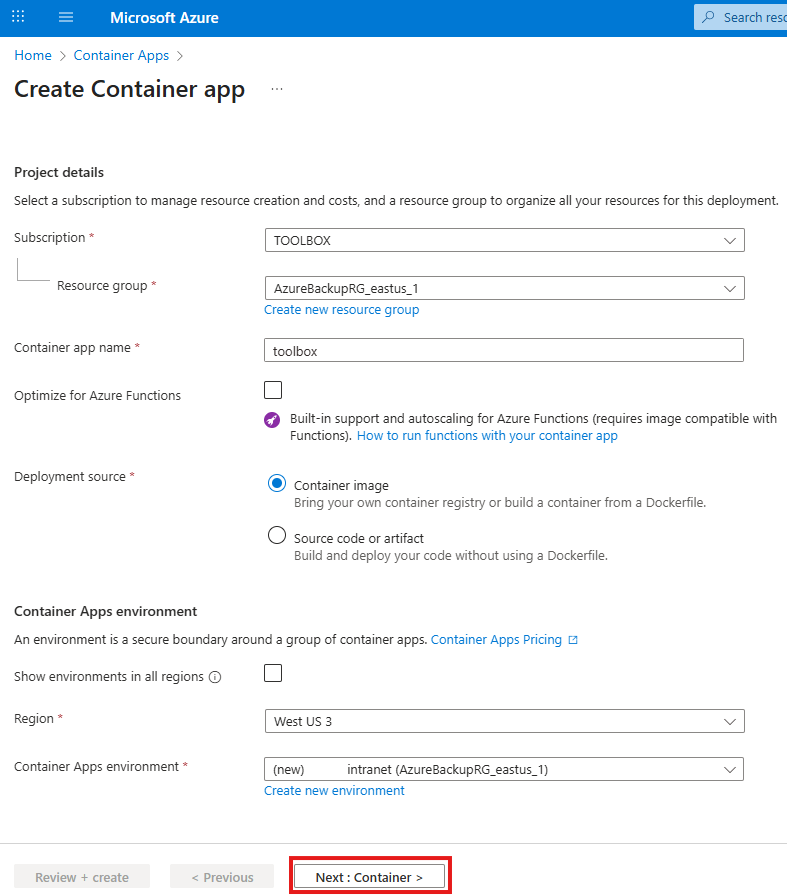
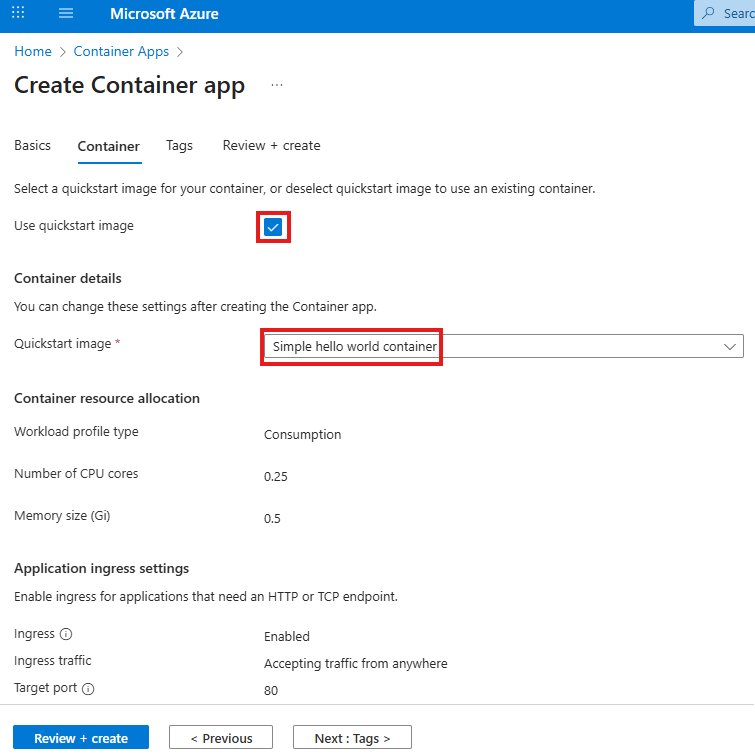
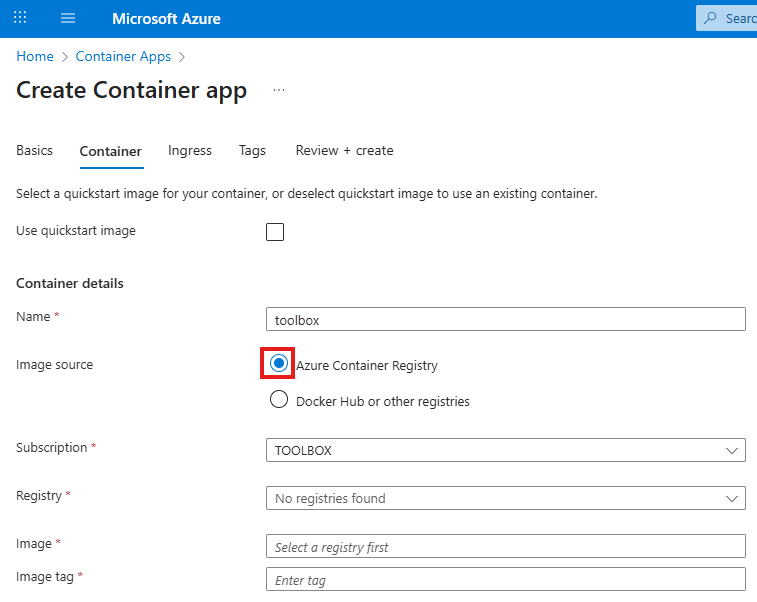
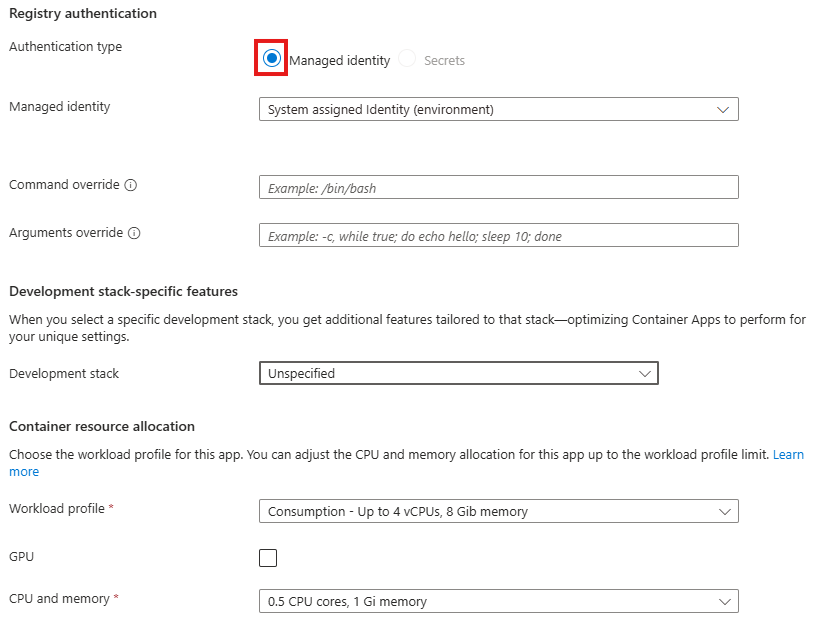
You may apply these configuration settings to enable useful features. Always read the documentation to see if these are safe and beneficial for you.
Copilot Memory
You can use Copilot Memory to remember repository context across Copilot agent interactions.
- On the https://github.com/settings/copilot/features page enable Copilot Memory
To store a memory start the prompt with “Remember: …”
More information on GitHub Copilot memories are at https://docs.github.com/en/copilot/how-tos/use-copilot-agents/copilot-memory