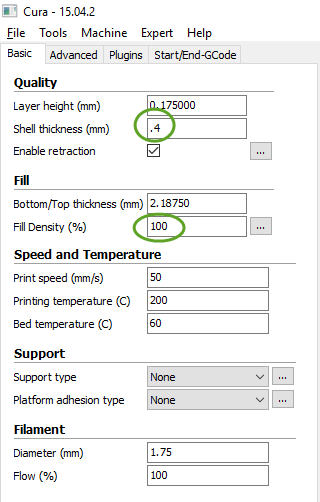
When you set the Shell Thickness too large, like 2 mm, Cura may generates hollow walls even if the Fill Density is 100%. To make sure the walls are solid, reduce the Shell Thickness to 0.4 mm and set the Fill Density to 100%.
Knowledge Base for IT Professionals, Teachers and Astronauts
When you set the Shell Thickness too large, like 2 mm, Cura may generates hollow walls even if the Fill Density is 100%. To make sure the walls are solid, reduce the Shell Thickness to 0.4 mm and set the Fill Density to 100%.

When you launch a new EC2 instance in the AWS cloud from the command line or with other cloud management platforms, you may get the error message:
CloudExceptions::CloudException – 400: VPCIdNotSpecified: No default VPC for this user (RequestID: …)
This can happen when the specified Subnet Id is not a valid subnet in the selected availability zone (datacenter).
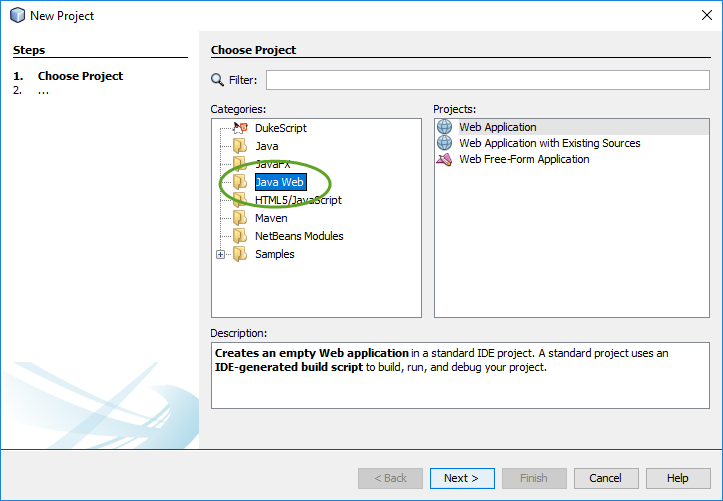
When you create your first Spring MVC Java web application in the base installation of NetBeans follow the steps below
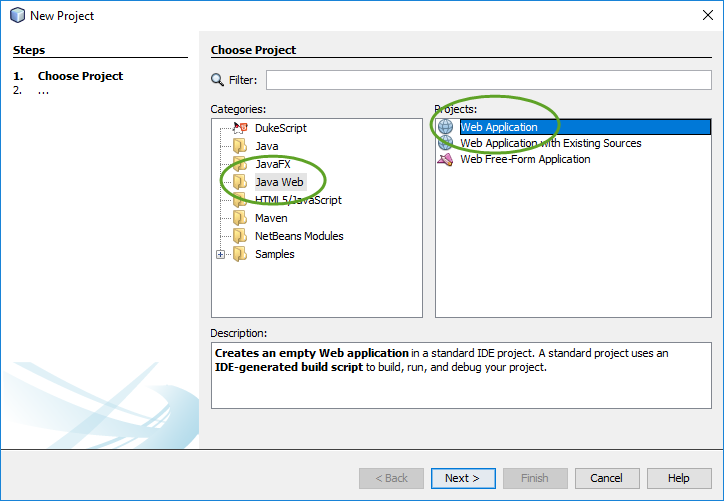
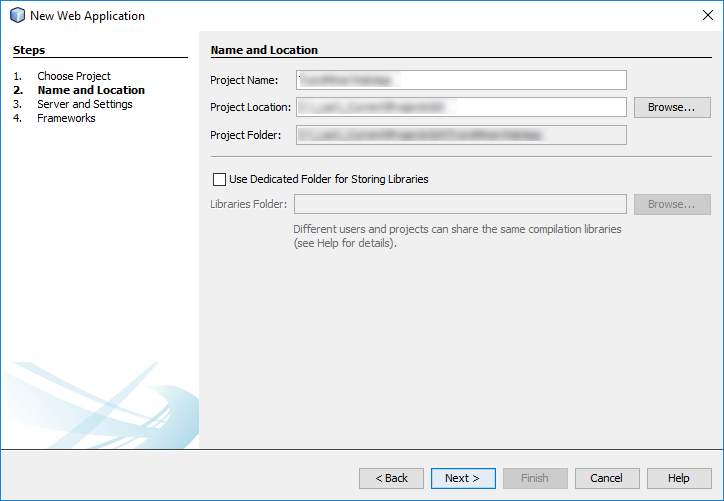
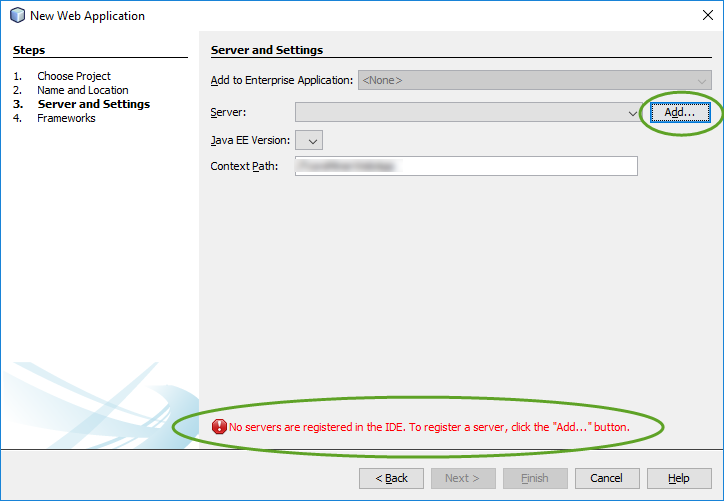
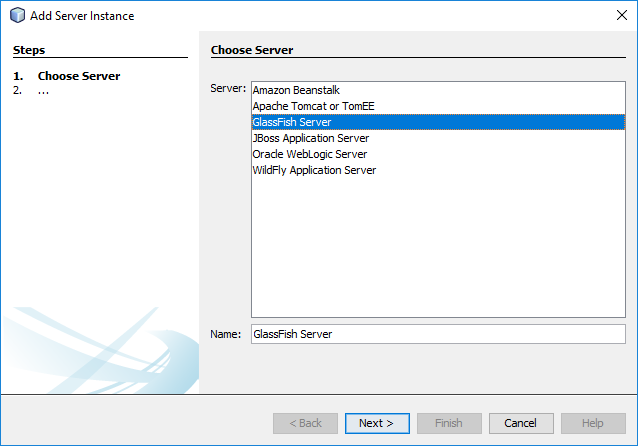
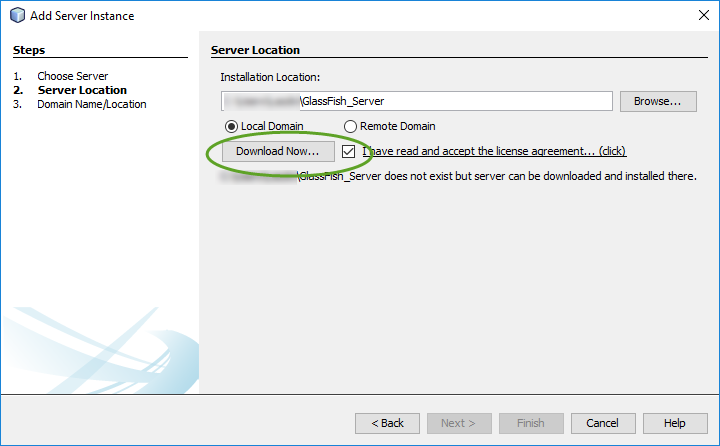
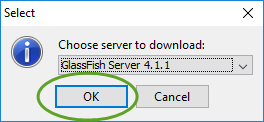
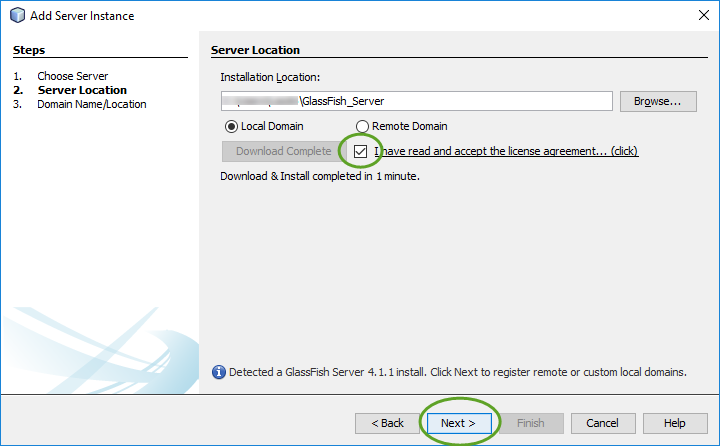
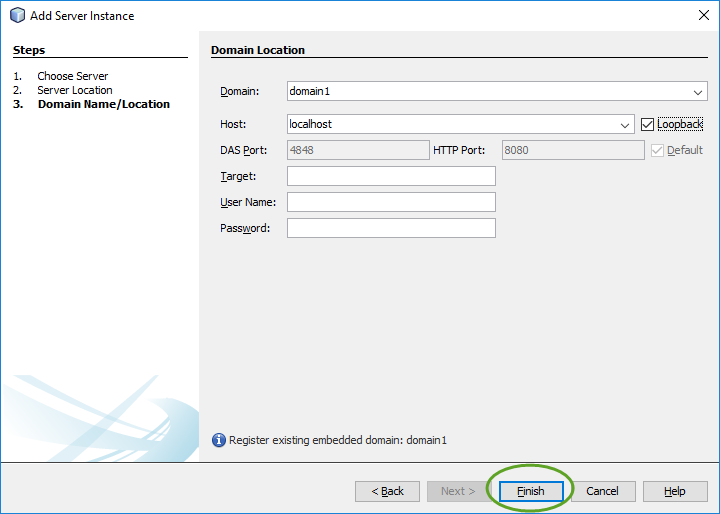
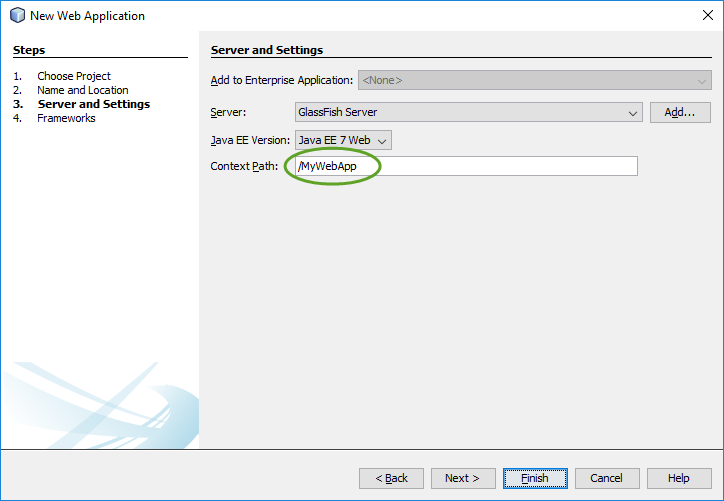
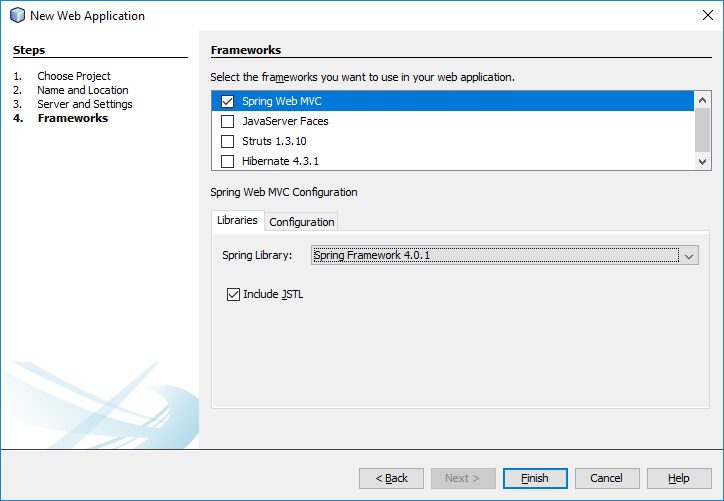
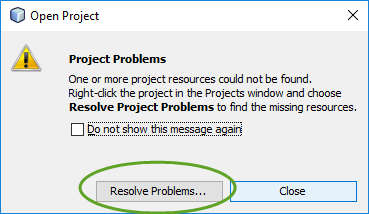
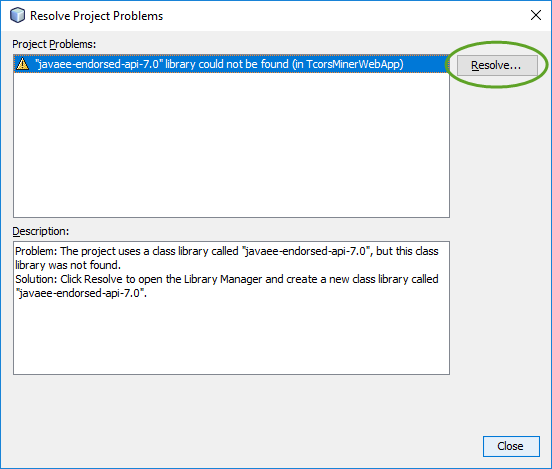
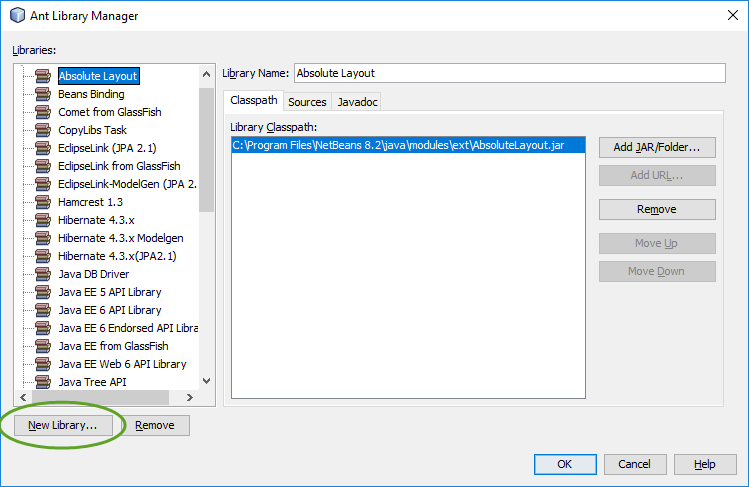
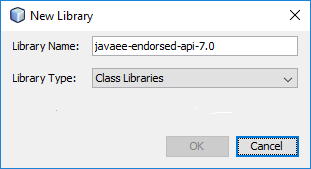
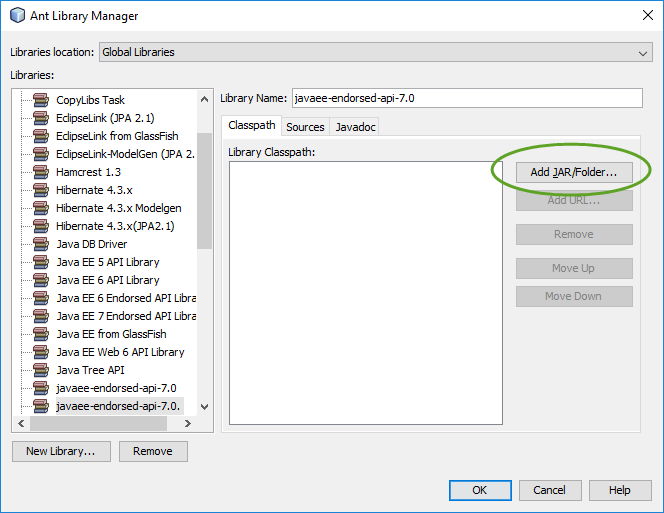
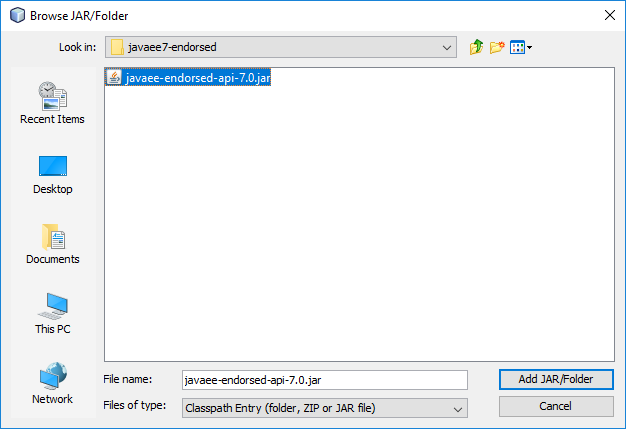
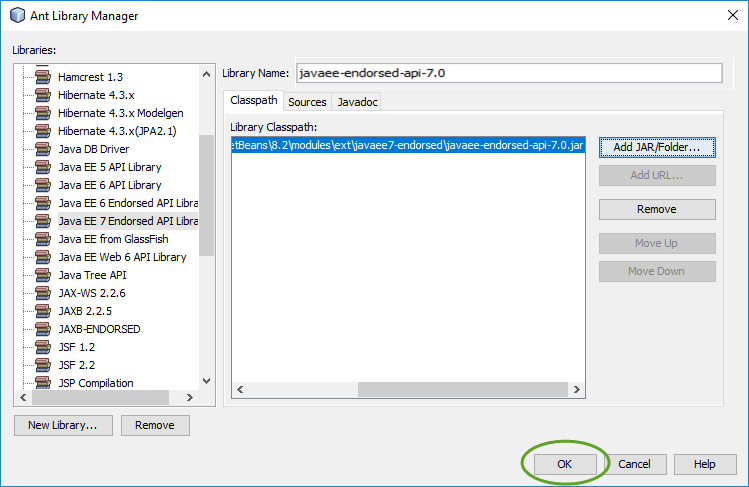
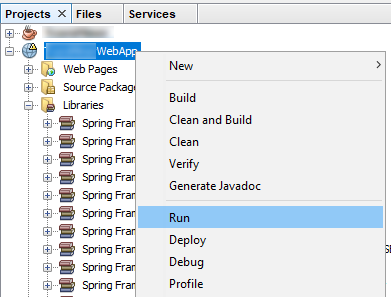
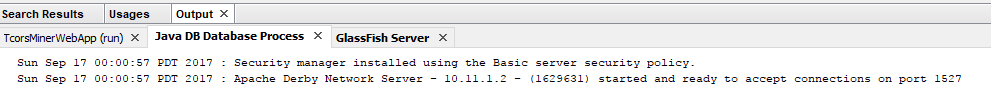
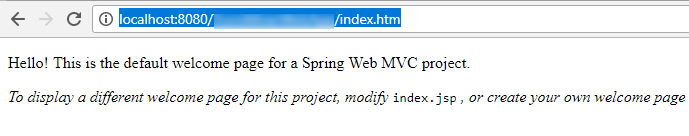
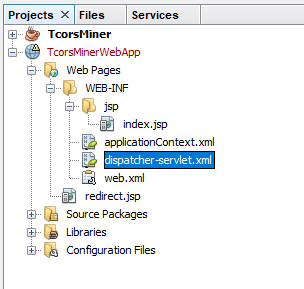
With the default settings the index.jsp composes the index page. It is in the Web Pages/WEB-INF/jsp directory.
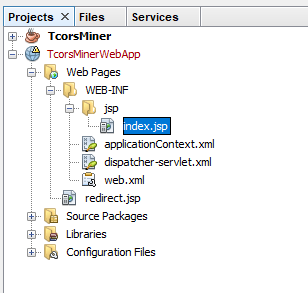
The web.xml file in the Configuration Files directory points to the first Java Server Pages file: redirect.jsp
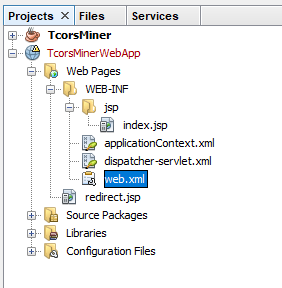
The redirect.jsp file is located in the Web Pages directory
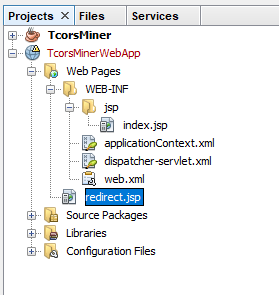
The dispatcher-servlet.xml file contains the mapping between the HTML file, controller, and view.
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<prop key="index.htm">indexController</prop>
</props>
</property>
The bean section specifies the name of the view for the controller.
<!--
The index controller.
-->
<bean name="indexController"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.ParameterizableViewController"
p:viewName="index" />
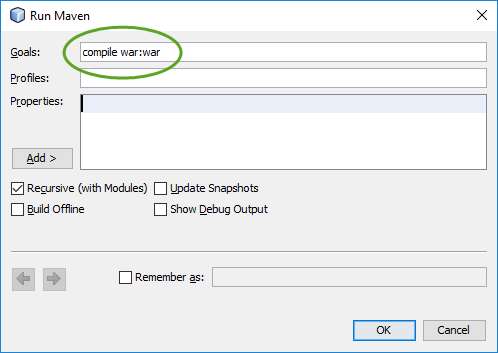
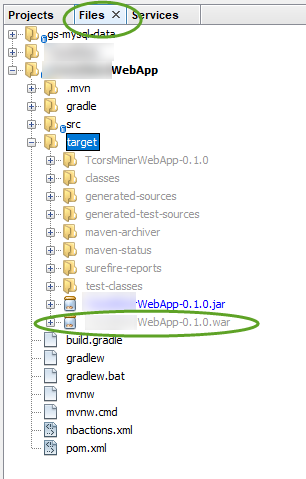
To generate a war file of your web application
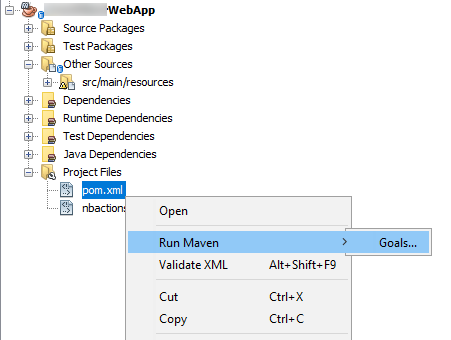
compile war:war
and click OK
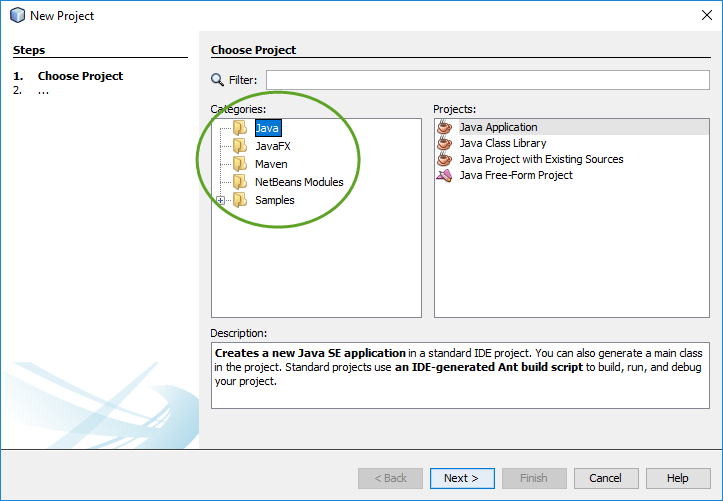
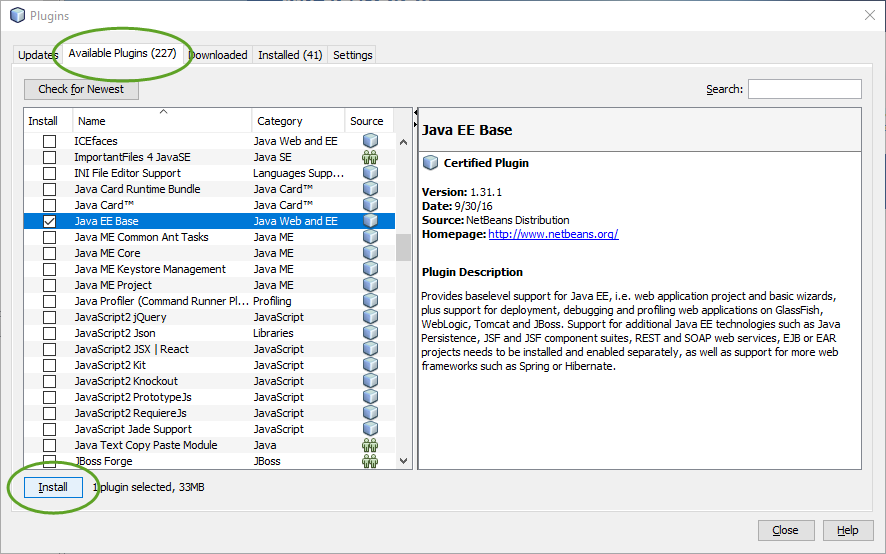
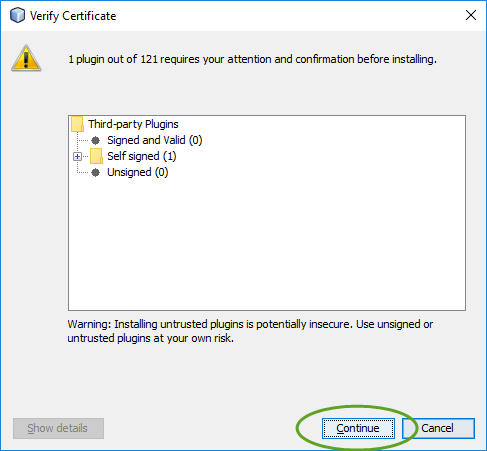
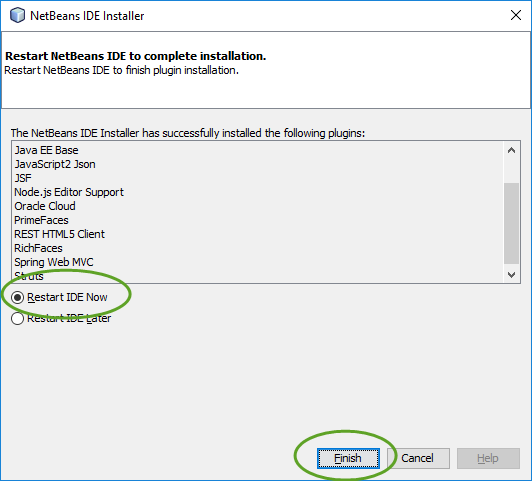
The base installation of NetBeans does not include the web development category.
To add the Java web development tools to NetBeans
When a process on a server instance needs access to an AWS account, the user who will execute the AWS CLI commands needs to be able to automatically authenticate in AWS.
For automatic AWS authentication, the AWS CLI creates two files in the .aws directory:
The location of this directory depends on the operating system and the type of user.
To create these files, you need to store the AWS Access Key and Secret Key. The safest place for these values is an encrypted data bag. To automatically generate the AWS files, create a data bag file and name it the same as the “id” in the following structure:
{
"id": "MY_DATA_BAG_ITEM_NAME",
"MY_PROFiLE_1": {
"region": "MY_REGION_1",
"aws_access_key_id": "MY_ACCESSKEY_1",
"aws_secret_access_key": "MY_SECRET_KEY_1"
},
"MY_PROFiLE_2": {
"region": "MY_REGION_2",
"aws_access_key_id": "MY_ACCESSKEY_2",
"aws_secret_access_key": "MY_SECRET_KEY_2"
}
}
To create and encrypt the data bag see my post on Chef Data Bags
# Iterate through the data bag and create the credentials file
puts "***** Creating the AWS credentials file"
# Load the encrypted data bag into a hash
aws_credentials = Chef::EncryptedDataBagItem.load('MY_DATA_BAG_NAME', 'MY_DATA_BAG_ITEM_NAME').to_hash
# Iterate through the items, skip the "id"
aws_credentials.each_pair do |key, value|
# skip the "id"
next if key == "id"
# Add the credentials to the .aws/credentials file
puts "Account #{key}, Region #{value['region']}"
batch "add_aws_credentials_#{key}" do
code <<-EOF echo #{value["aws_access_key_id"]}> input.txt
echo #{value["aws_secret_access_key"]}>> input.txt
echo #{value["region"]}>> input.txt
echo.>> input.txt
aws configure --profile #{key} < input.txt
EOF
end
end
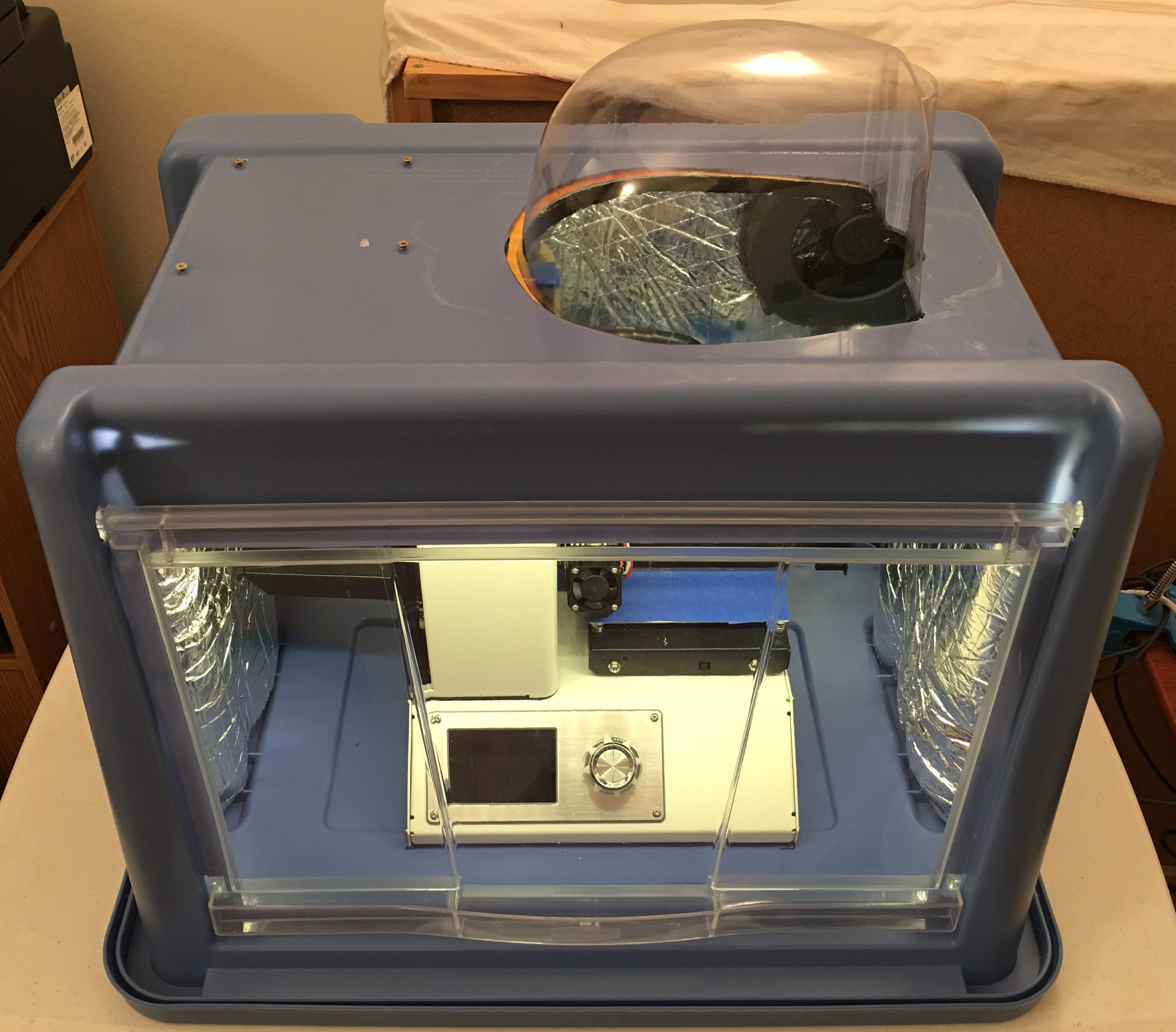
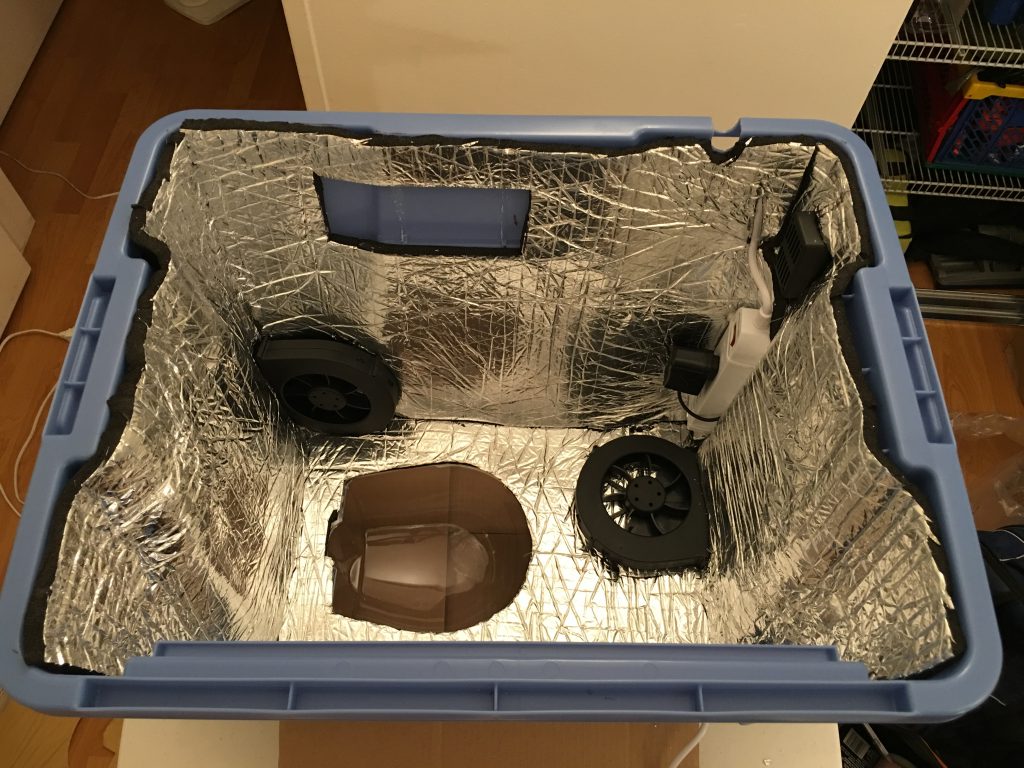
The Monoprice Select Mini printer is an open design, all noise making parts are exposed, and as the stepper motors move the head and the platform, the vibration transfers to the table it is sitting on. There are a few sound proof enclosure designs on the internet, but I have found one that looks cool and easy to assemble. The original design doesn’t use the lid as a platform, but as I found out, the lid on flexible legs and the soft foam insulator under the printer greatly reduces the vibration transferred to the table. My family doesn’t even notice anymore when the printer keeps working overnight on a large model. Without the enclosure, I always had to make sure the printer stopped before bedtime.
The enclosure provides significant noise reduction. I have used an iPhone app to measure the noise from 1 meter distance. The 6dB difference doesn’t look too much, but on the logarithmic scale that means half volume reduction.
I could not measure much difference in noise levels with and without the insulator on the door, but during night printing even a small reduction in noise level counts.
My version of the soundproof enclosure for the Monoprice Select Mini 3D printer is based on the great design announced by Daniel Smith at https://www.thingiverse.com/groups/monoprice-select-mini-owners/topic:16820
The original build instructions are at http://imgur.com/a/1571B
In this post, I will show the modifications I made to the original design. Read the original article for more information.
I re post the bill of materials in case the original article disappears:
The total cost of my version is about $150, though you can eliminate a few of the line items to bring the cost down if needed. Ended up not buying the web camera, as I can check on the progress anytime by walking to the printer. Maybe later I will buy it to create time lapse videos.
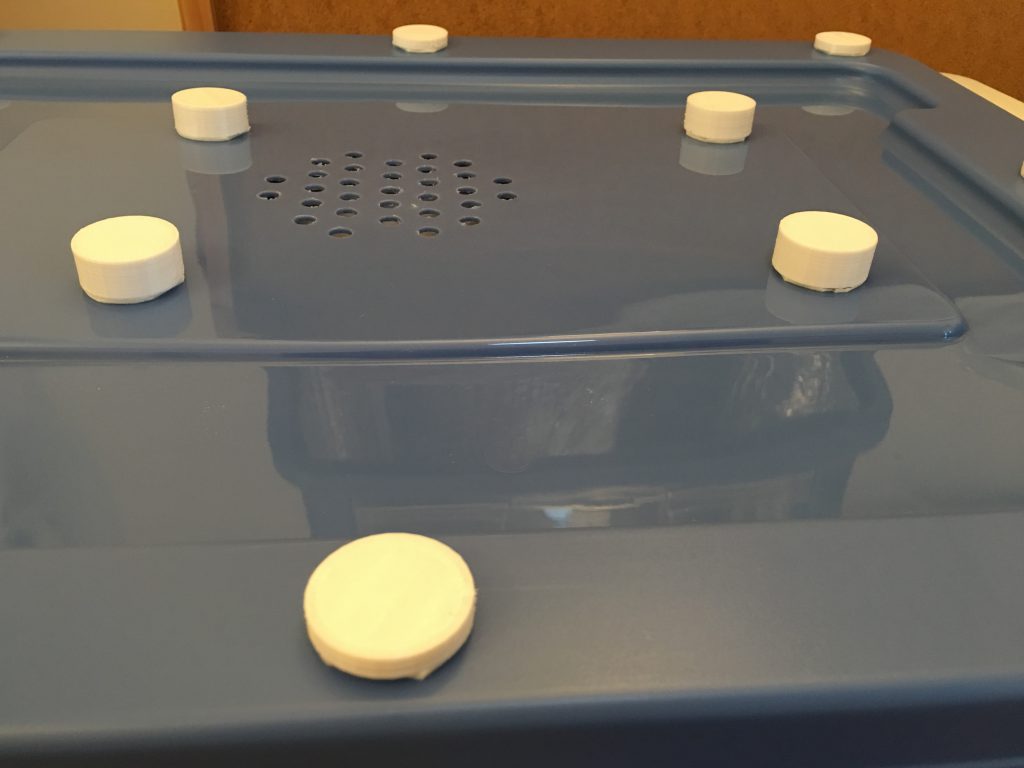
The major differences are the transparent dome on the top and using the lid as the bottom of the box. The dome serves two purposes: Room for the tube at the top of the head, and provides a great view of the 3D object on the platform during the printing process. The lid provides the needed alignment when I put the box above the printer because the build platform almost hits the front and the back of the box.
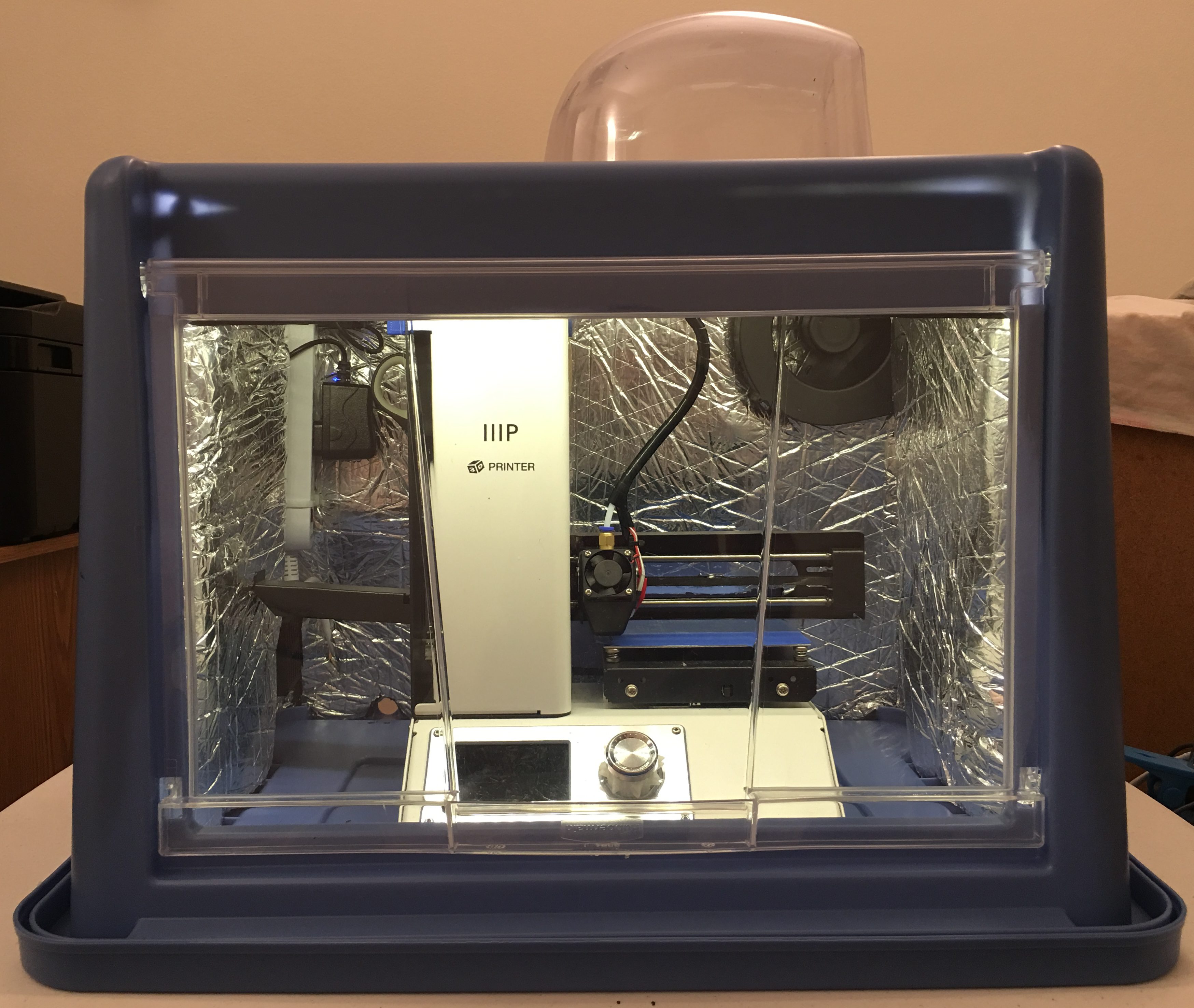


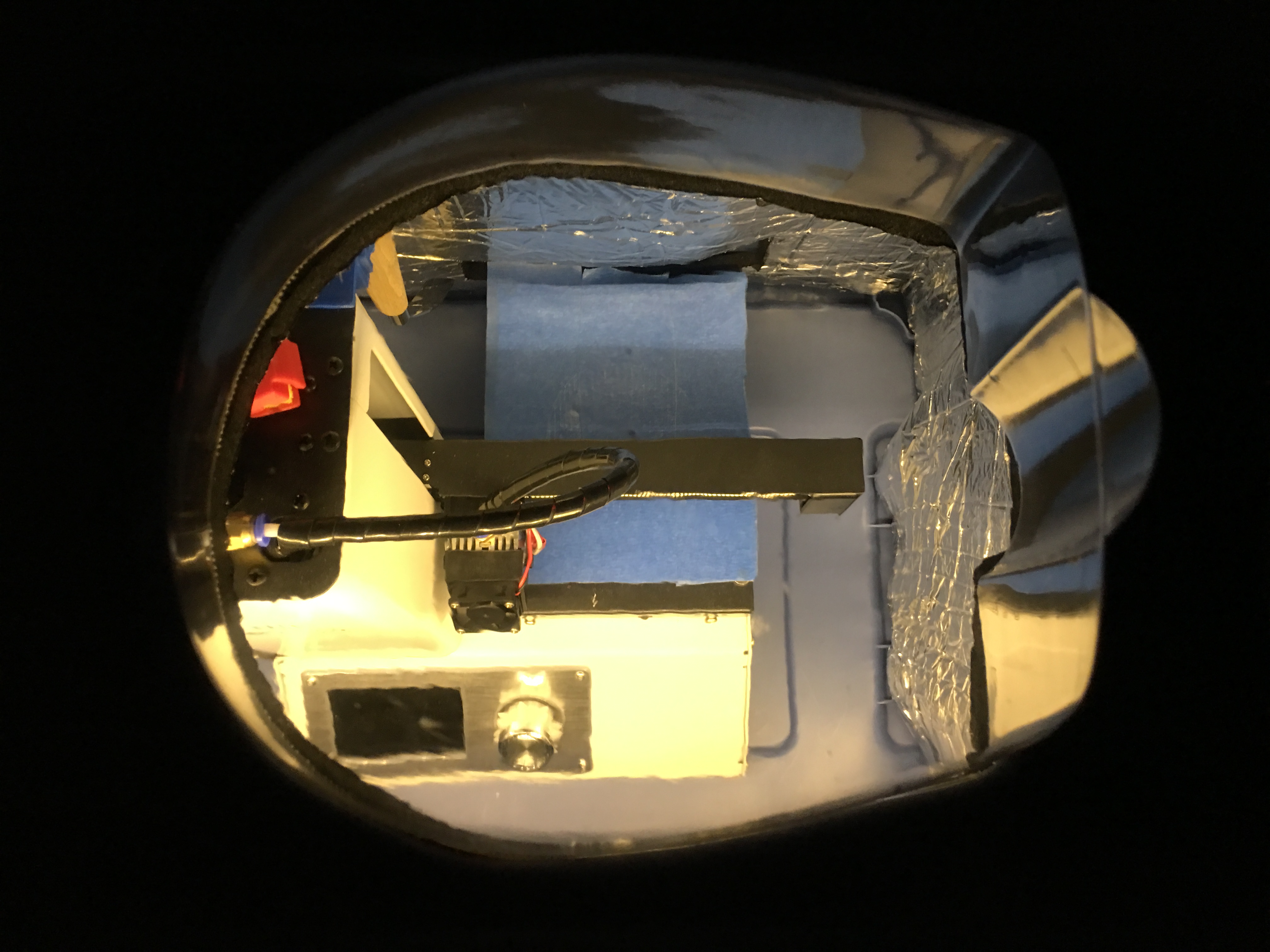
Measure twice, cut once told my father, and he was right. The original author already warned us, because the box sits above the printer upside down, it is very easy to cut the openings on the wrong side of the box. I have started the process with a permanent marker and marked all openings on the box. Before cutting the material, I placed the box above the printer and verified the location of all of them.
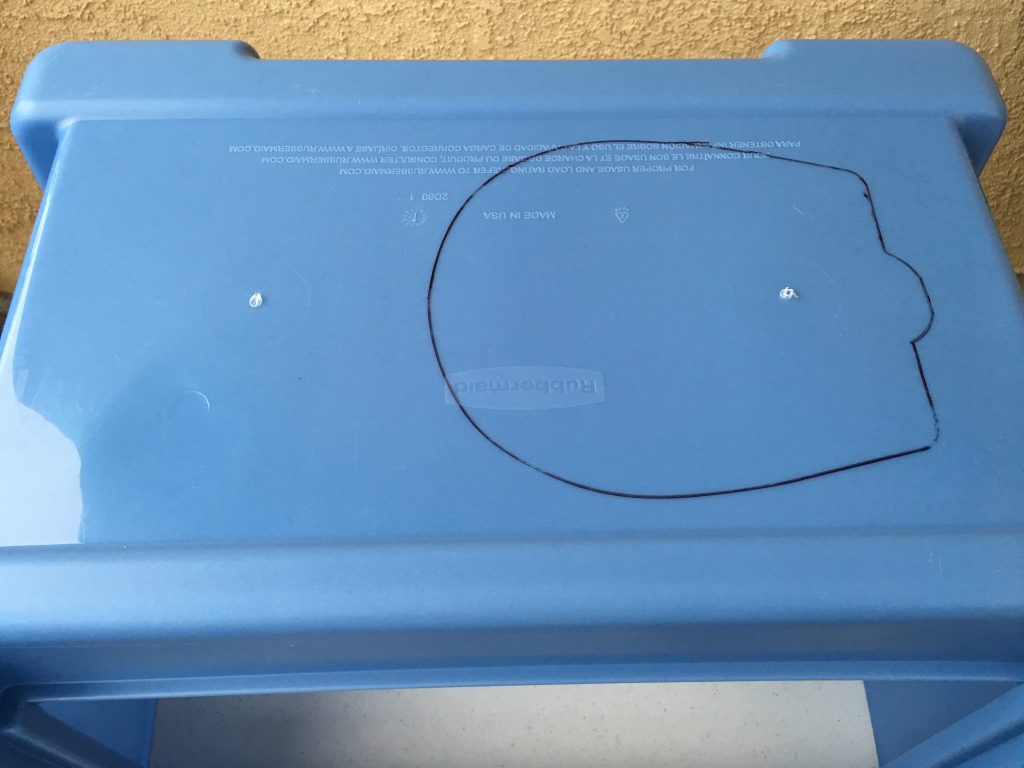
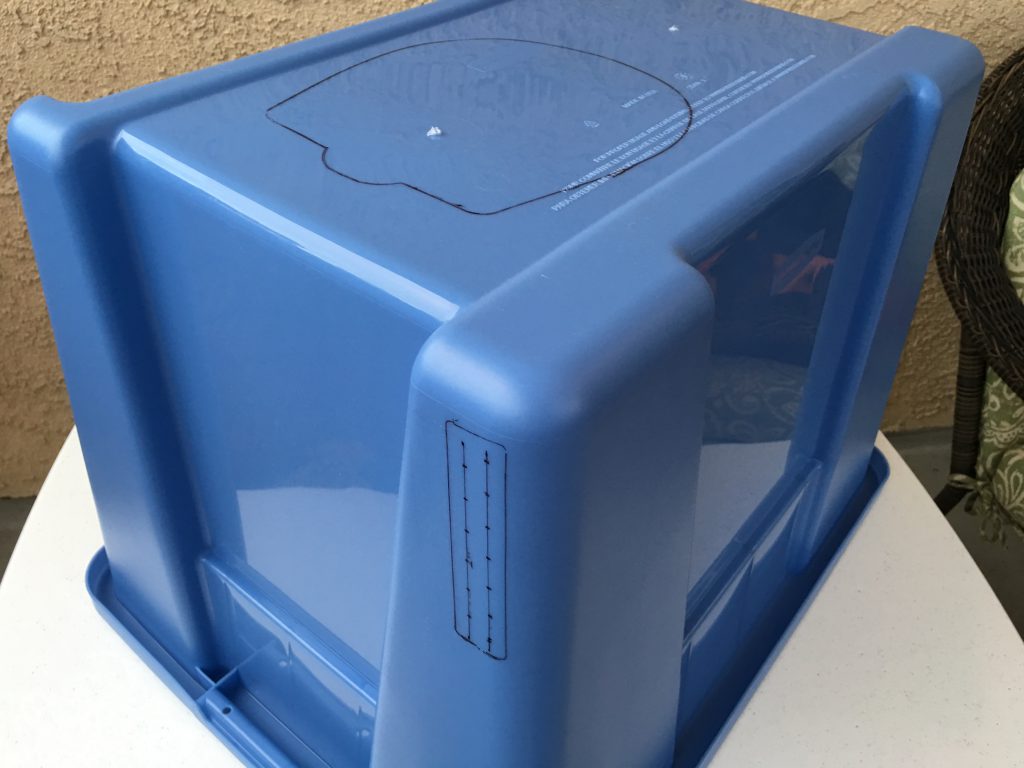
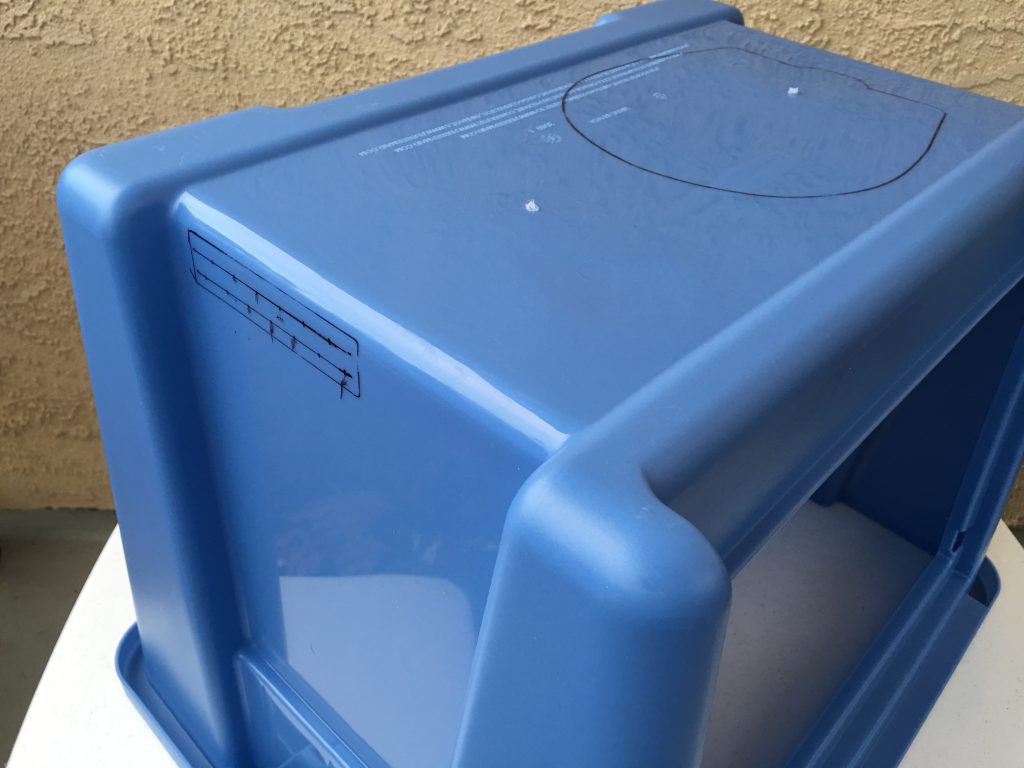



When the head is at the highest position, the feeding tube needs more room than what the plastic box provides.
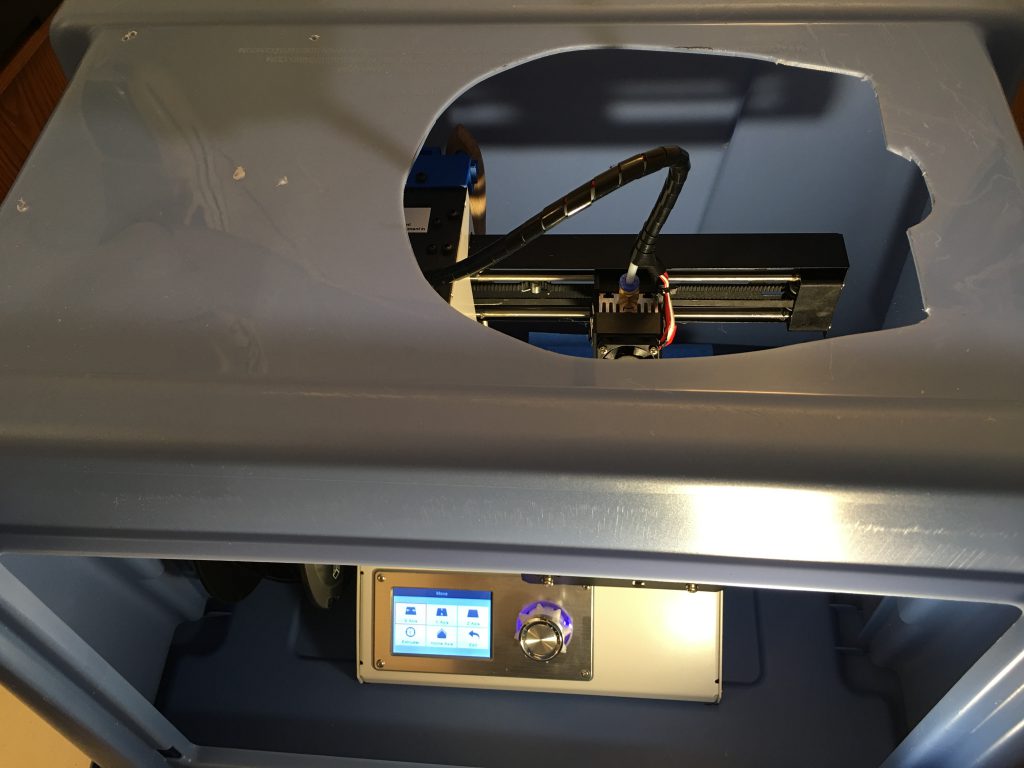
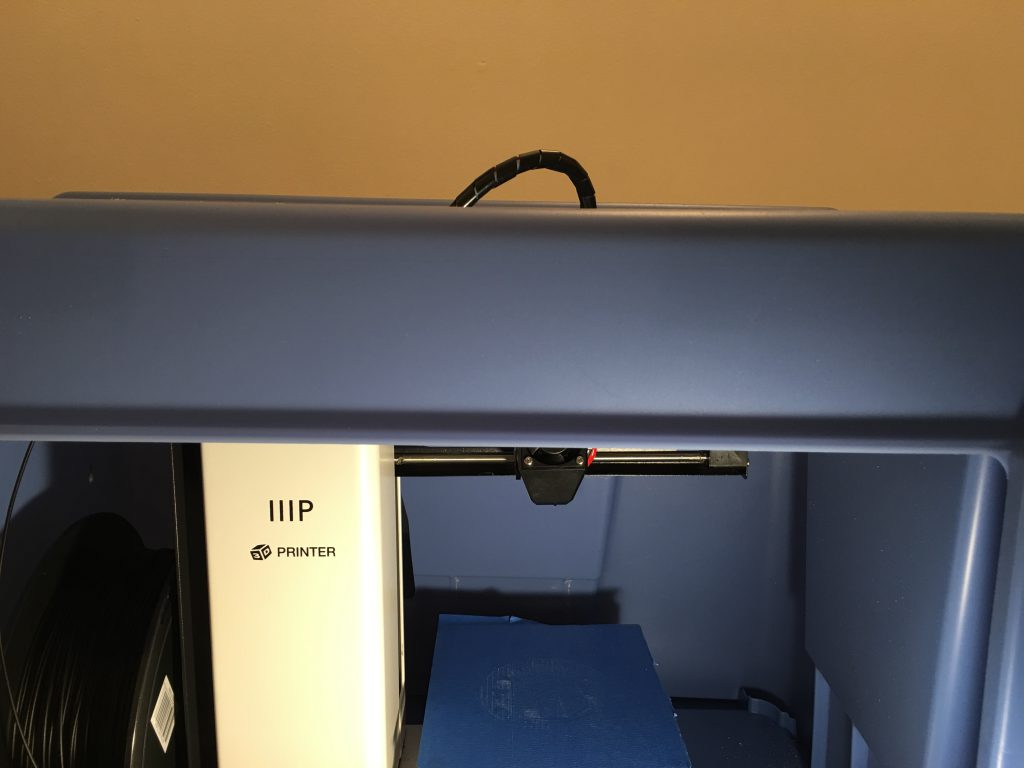


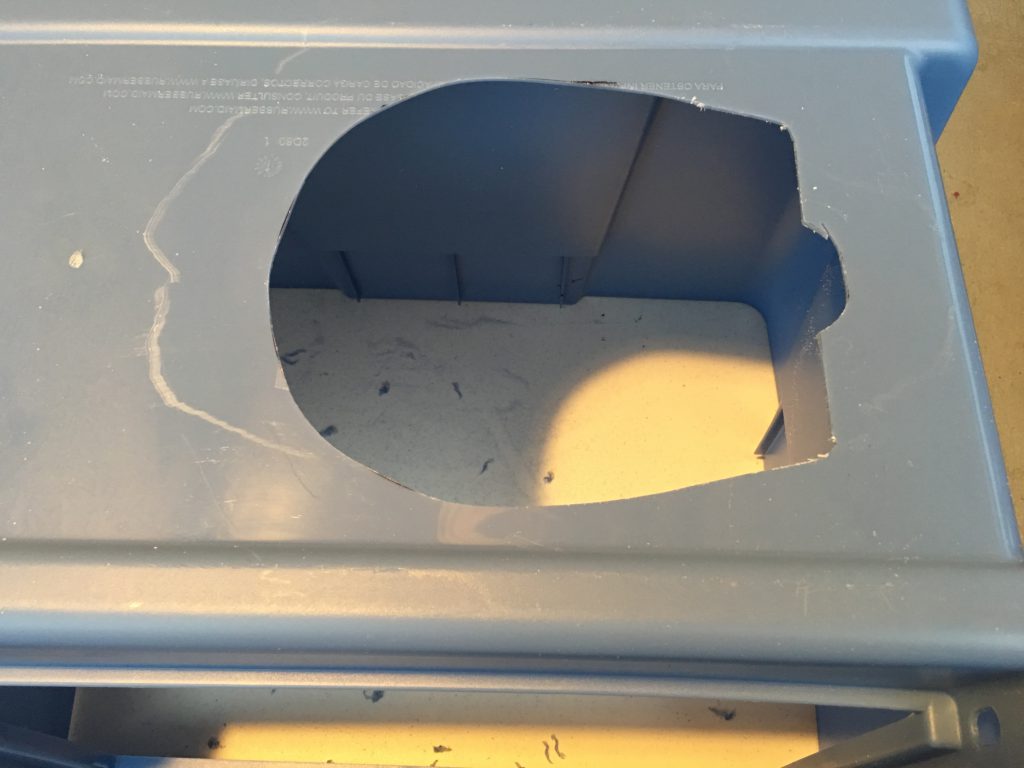
The transparent dome is the packing material of a large headphone. First I cut the opening for the dome with an electric jigsaw.

The distance between the hole centers is 15 mm, drill the holes with 8 mm drill bits.
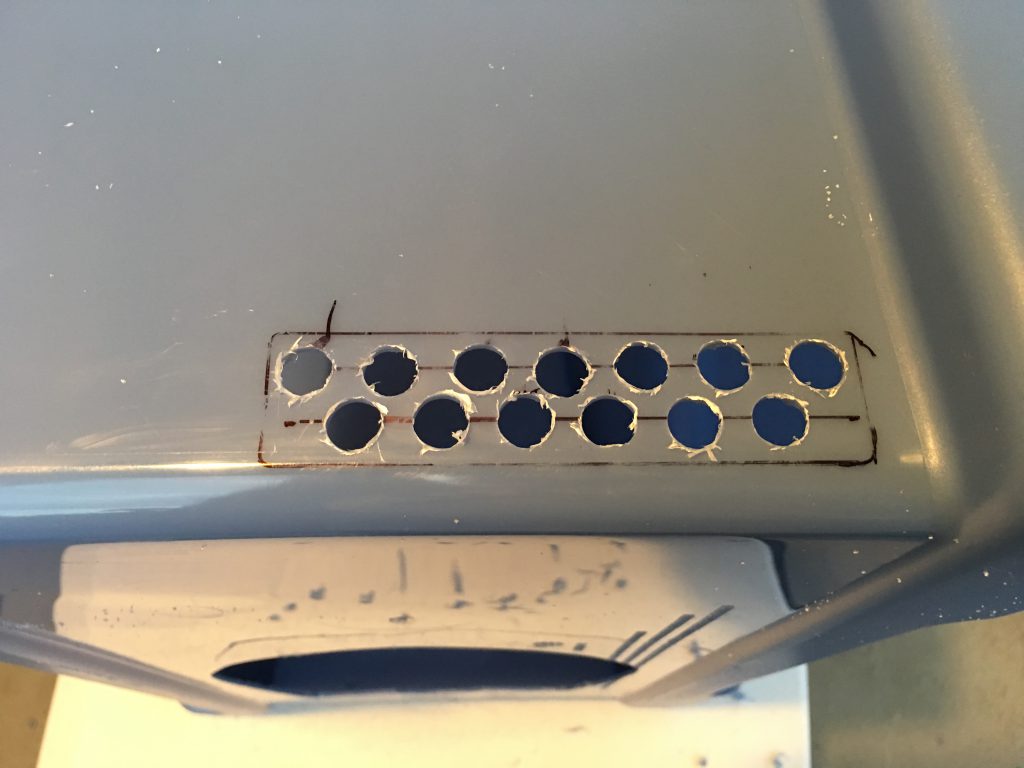

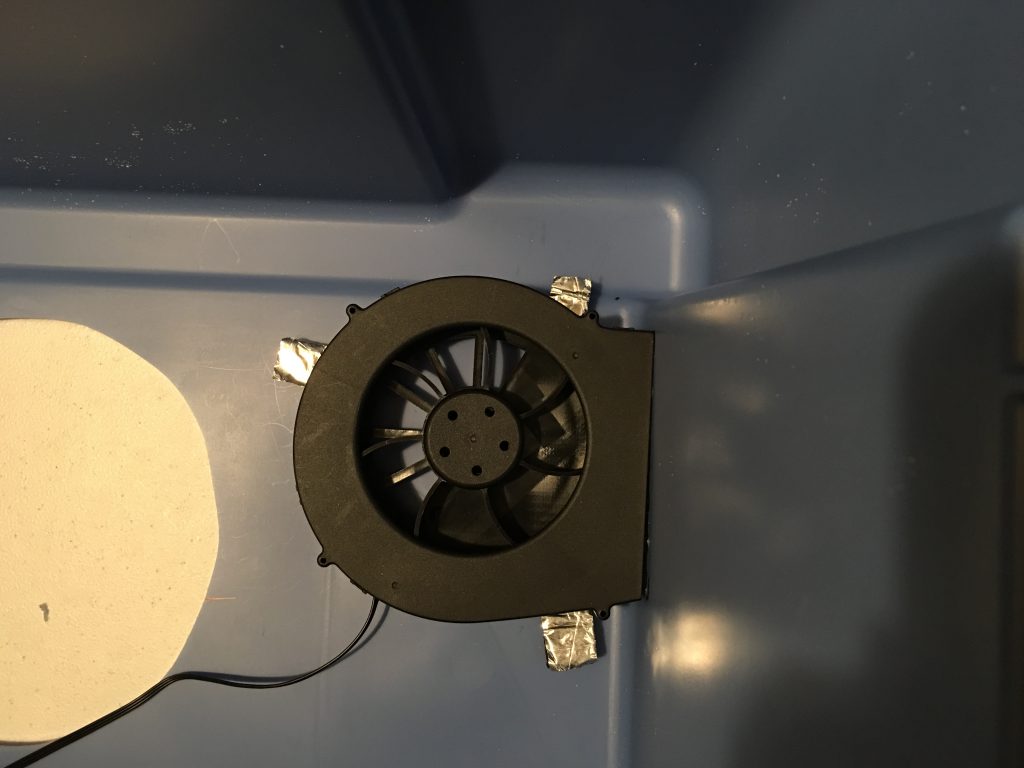
The original plan recommended Super Glue to mount the fans, I wanted a more secure hold, so I used thin wood screws to attach the fans to the box. To mark the location of the holes I inserted the screws into the mounting holes of the fans, painted the heads with the permanent marker and quickly pushed them to the planned location inside the box. After a few tries, I could see the screw locations on the walls. I enlarged the marks with a thick permanent marker and using a flash light copied the locations to the outside surface. To get the correct position I used small strips of the insulating material under the blowers because those will be on the surface of the insulator.
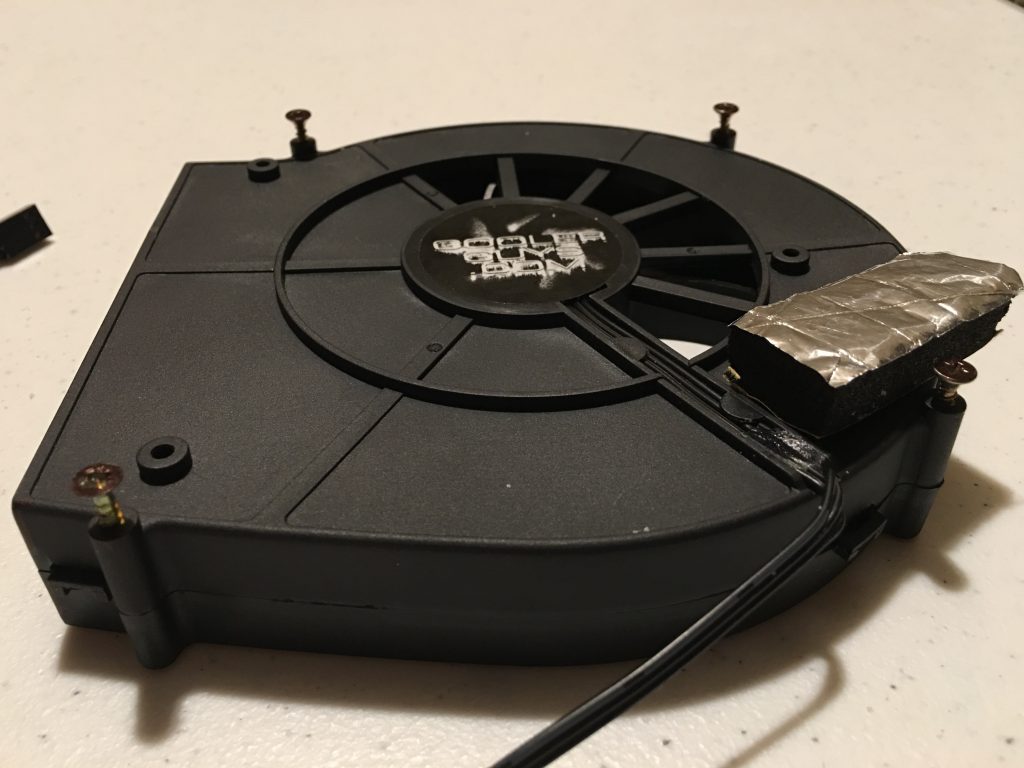
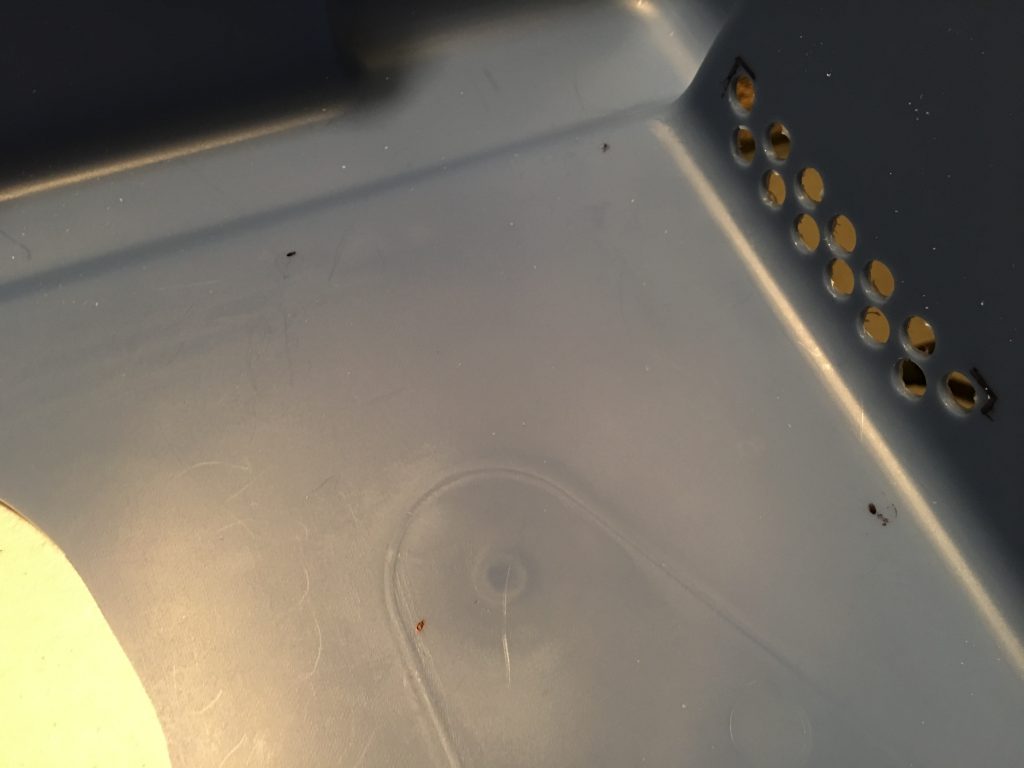


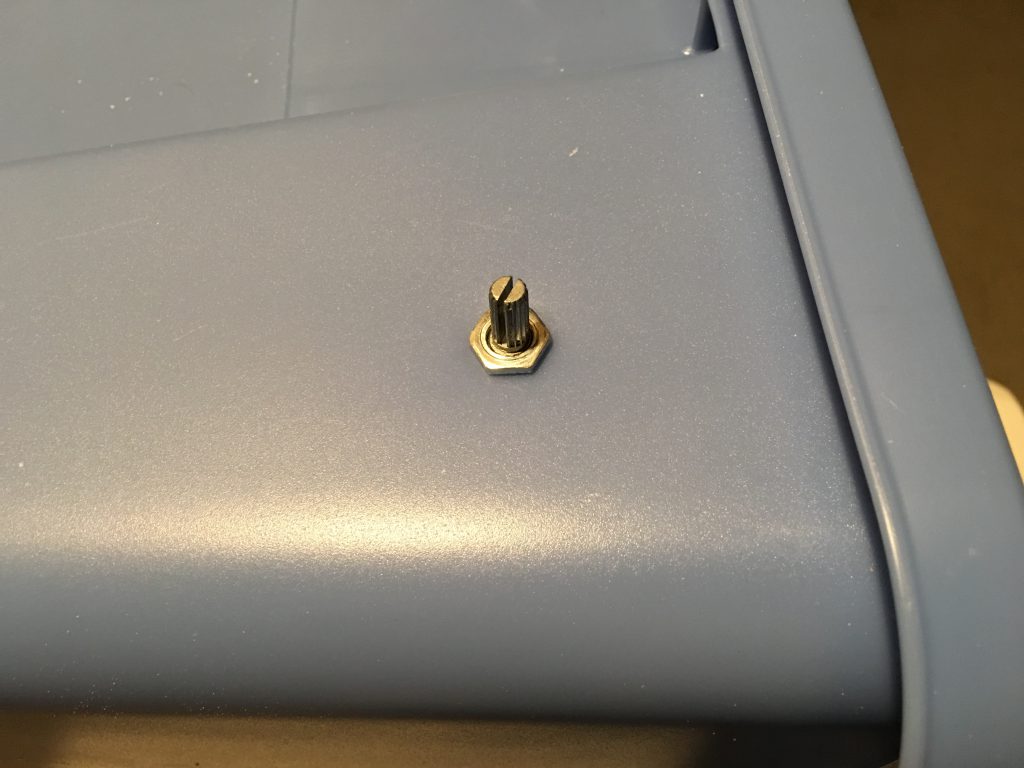
I drilled a hole for the potentiometer of the speed controller and used the nut to secure it below the power strip on the left side.
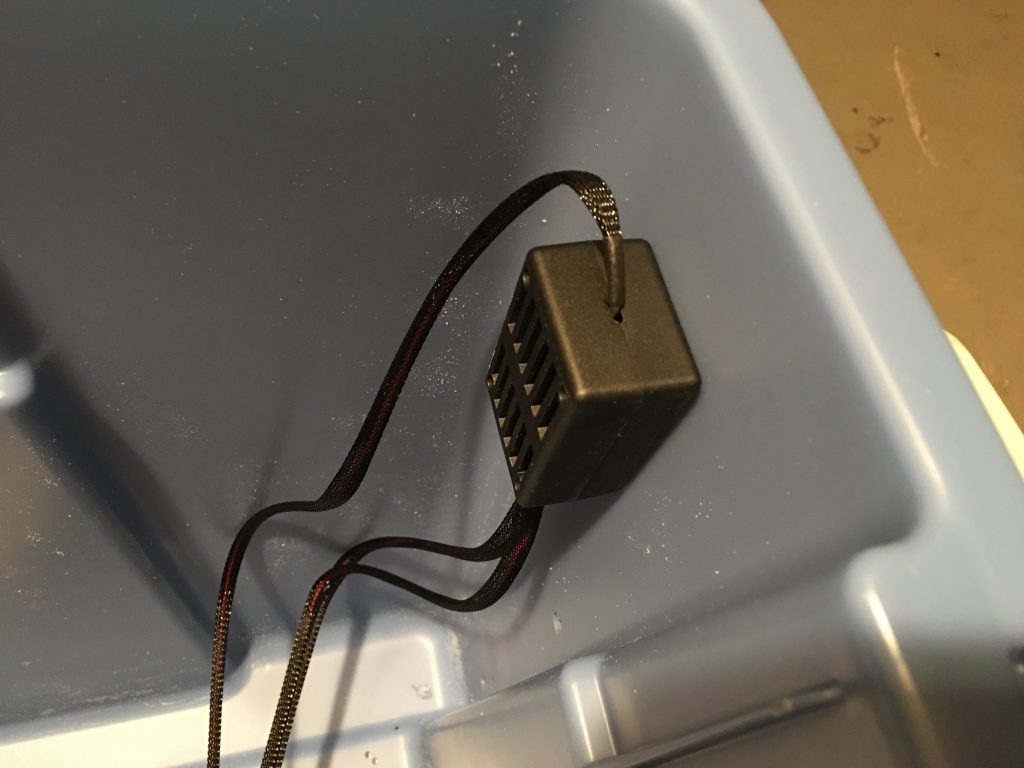


Drilled four holes for the zip ties and cut a square opening with a Dremel tool for the plug.
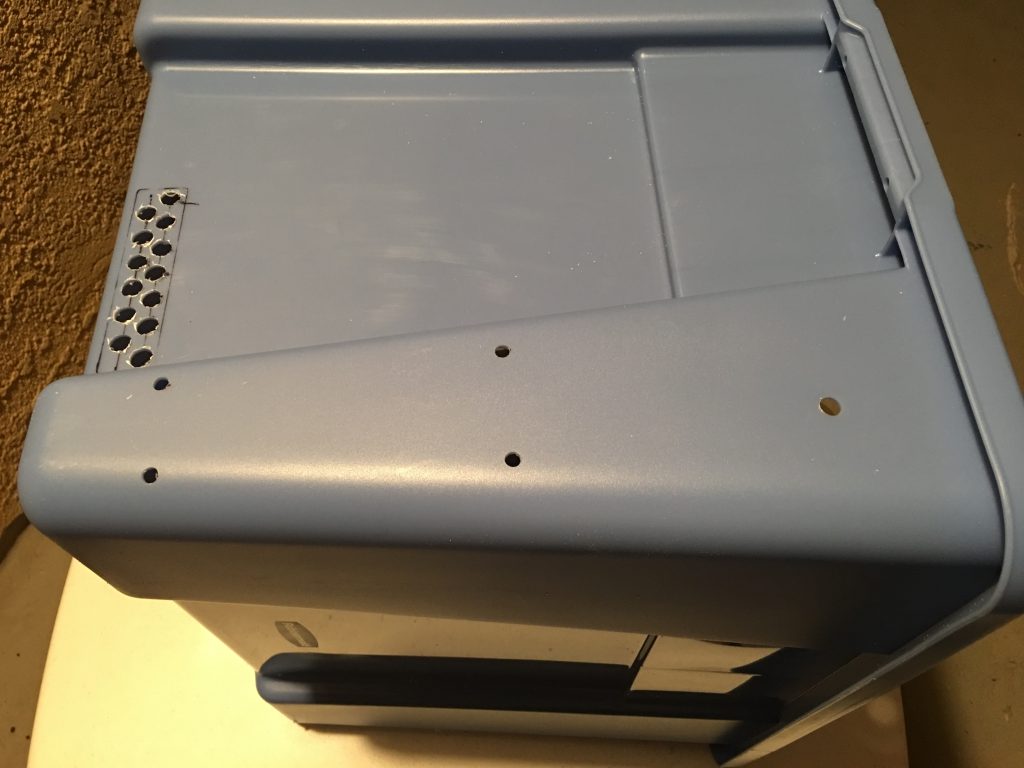
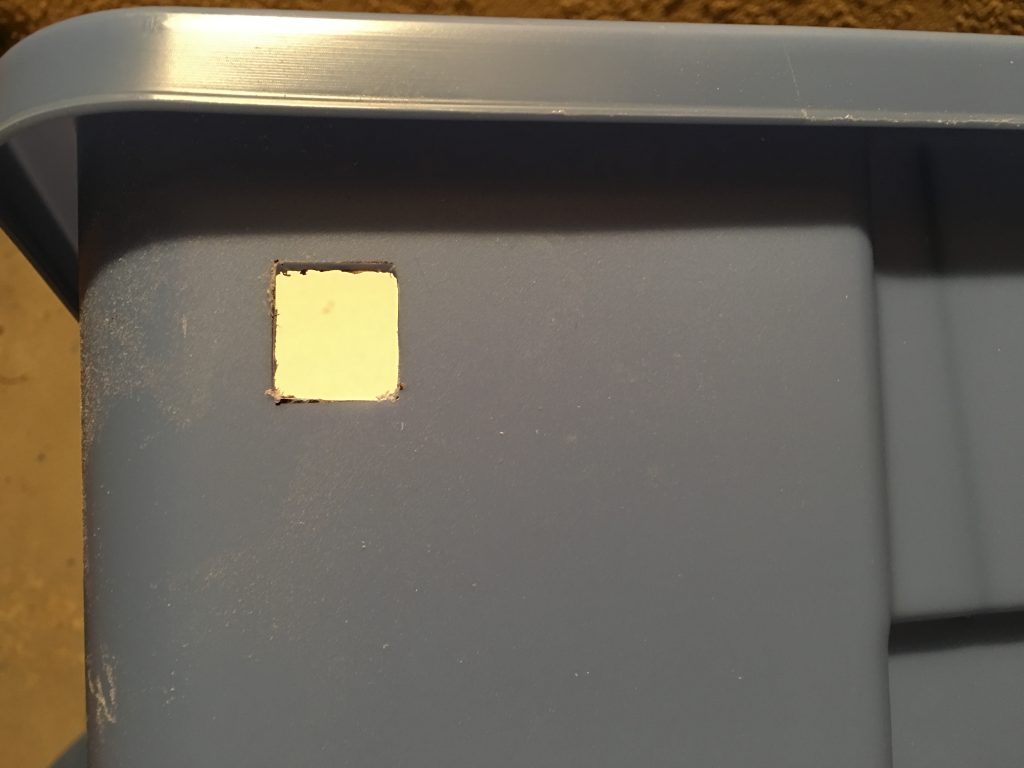



THe build platform almost touches the front and the back of the box. To make more room at the back I used the same Dremel tool to remove the ribs from the back of the box.
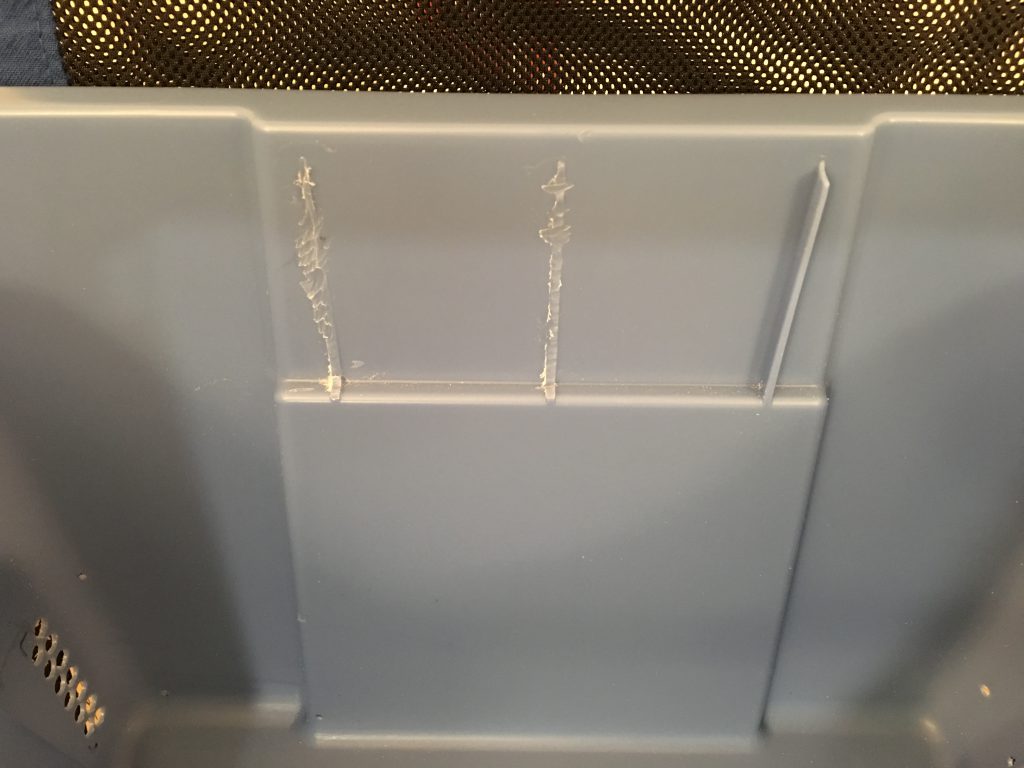

To change the filament, replace the blue painter’s tape on the build platform, or remove a large object, I frequently have to lift the box. To easily position the box over the printer, I use the lid as the base under the printer. To be able to easily remove the box and place it on the floor, the power strip only provides power for the blowers and the LED strip ( I haven’t installed the camera yet ), I left the power supply of the printer outside of the box and plugged it separately into the wall outlet. I used a 5/8″ wood bit and the Dremel tool to enlarge the hole for the barrel plug.
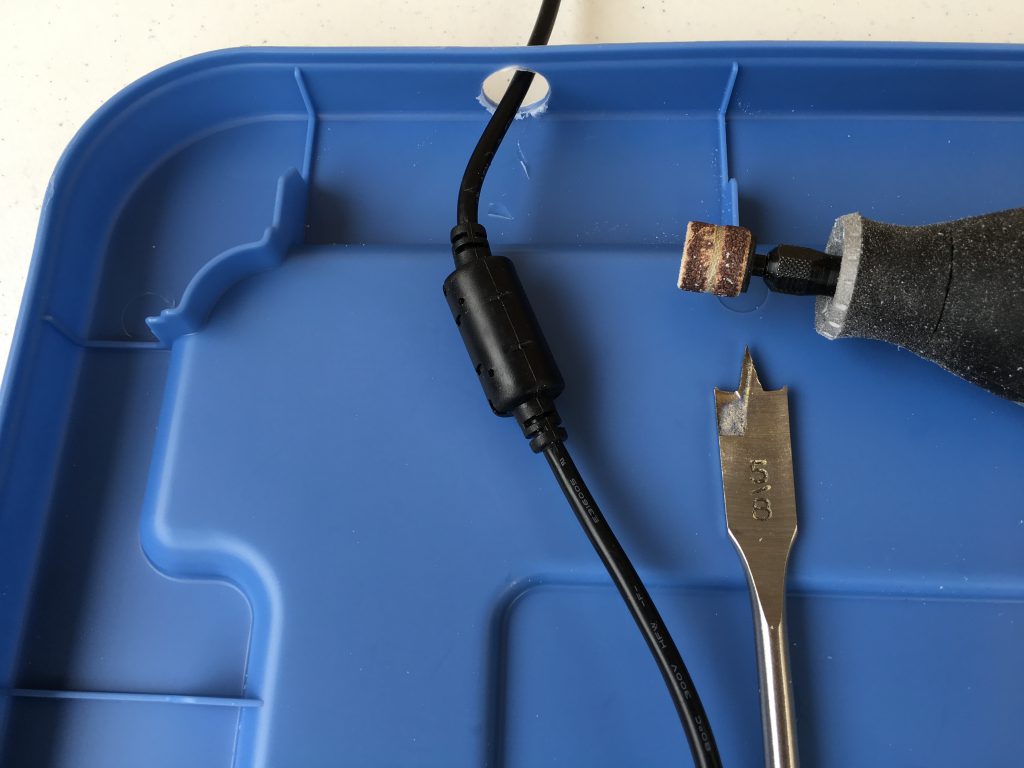

I also drilled two holes for the cable tie to secure the power cord to the lid.
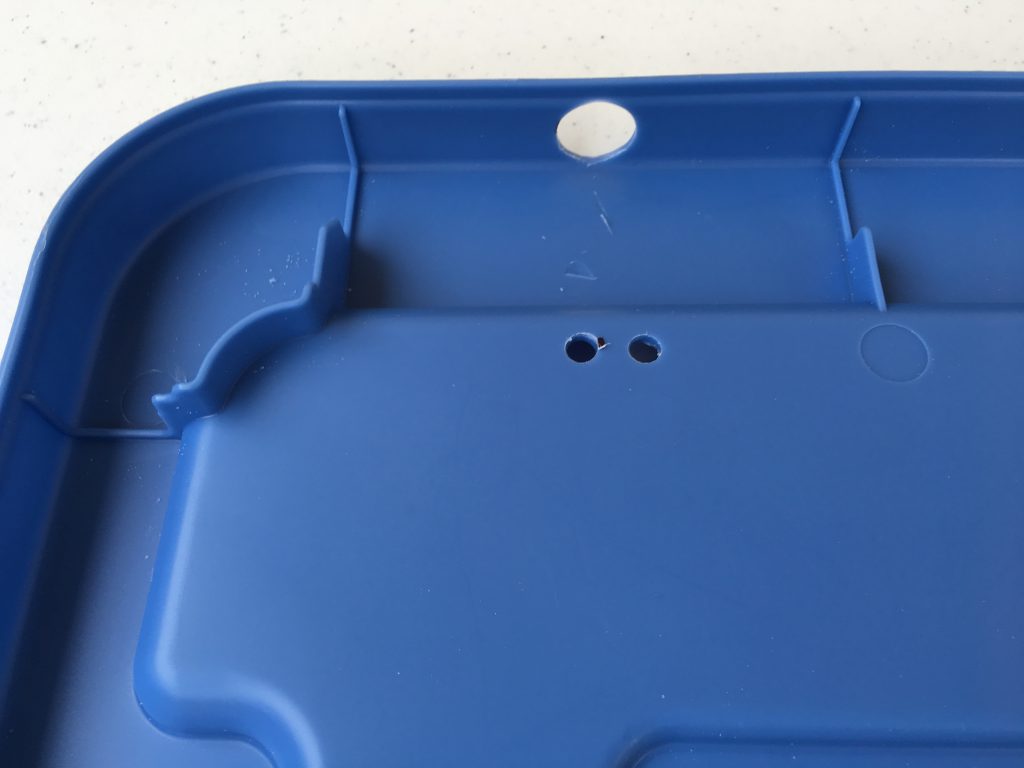

I also had to cut into the edge of the box where the printer power cord enters the box.
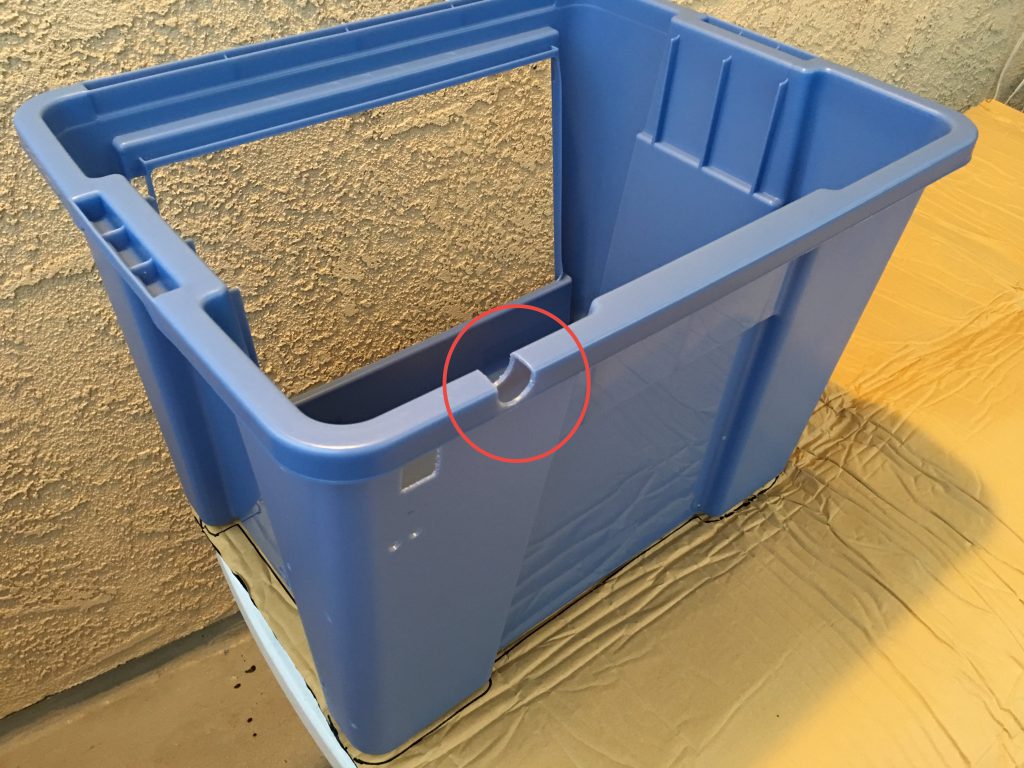
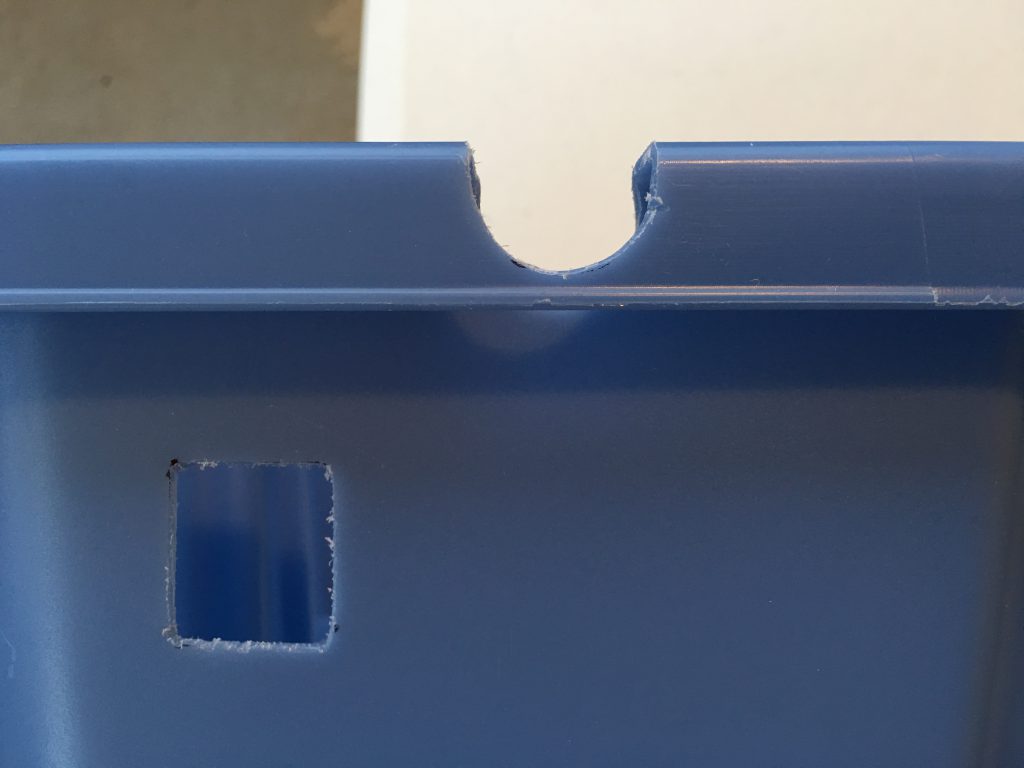
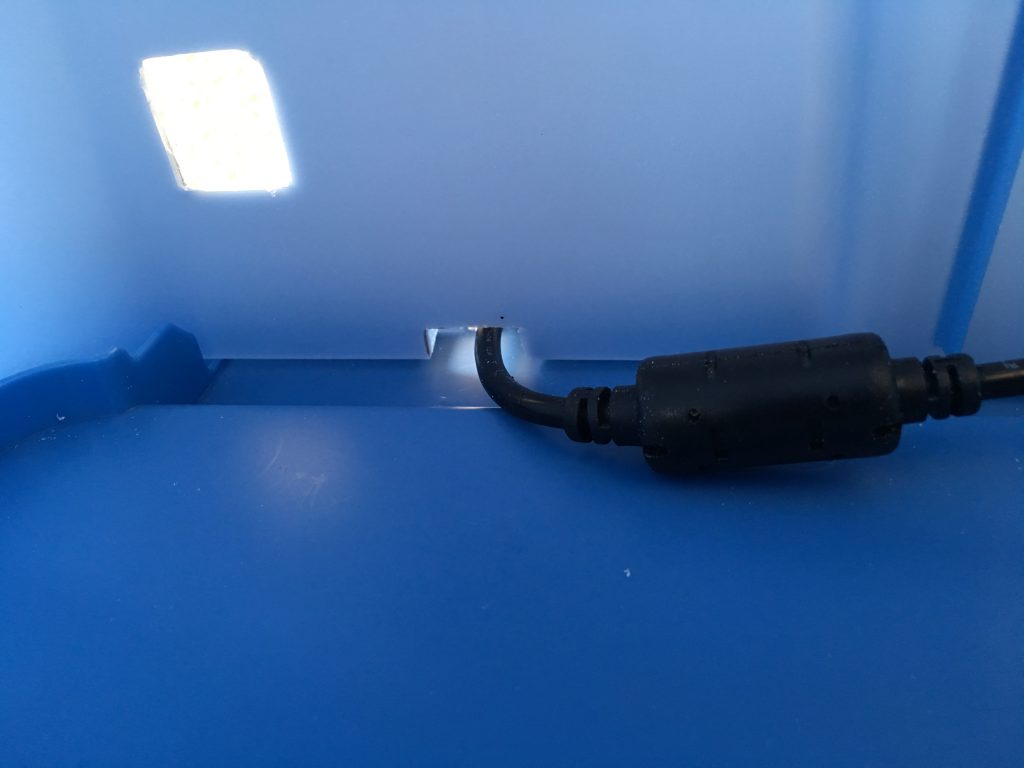
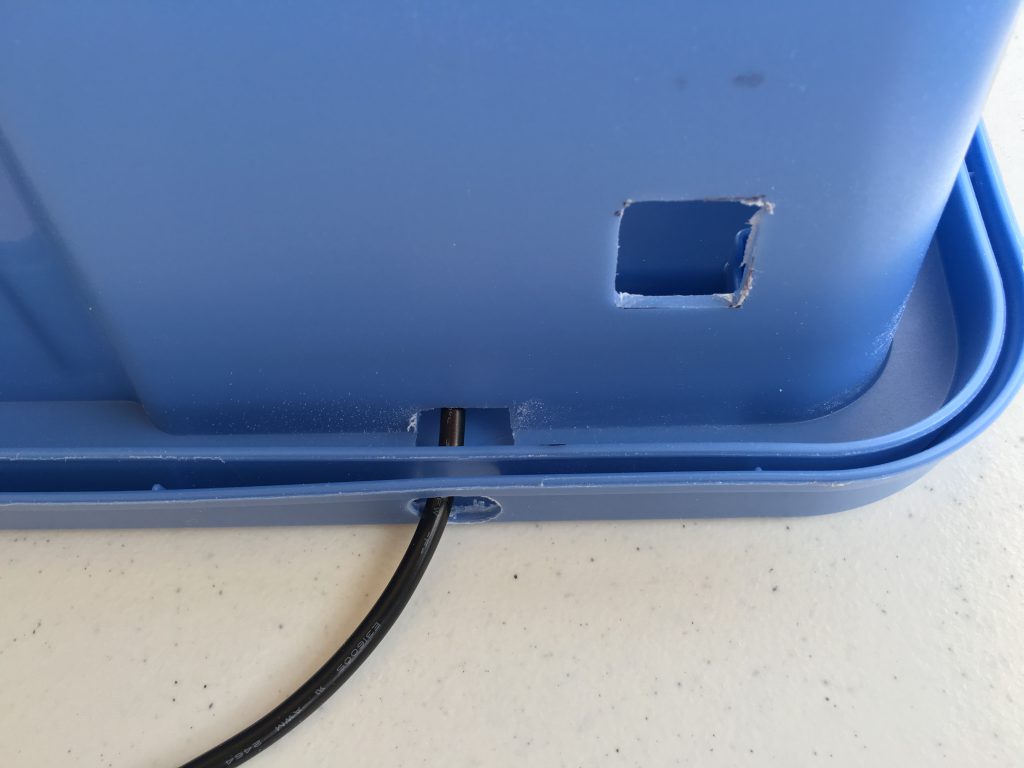




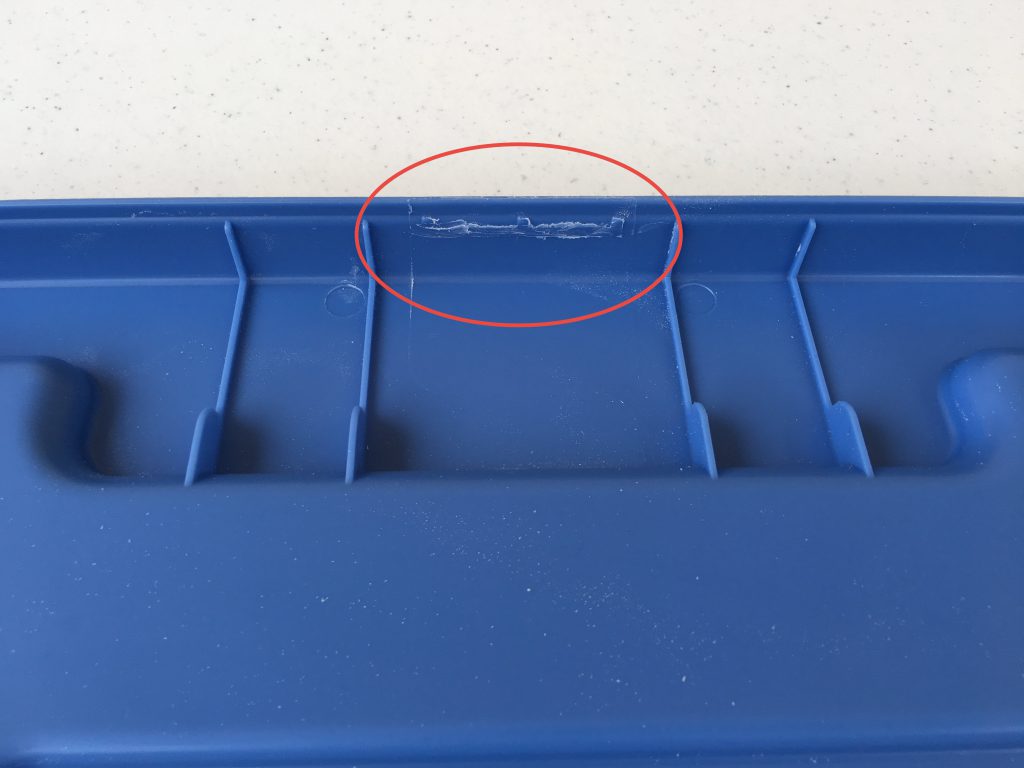
To be able to easily lift the box, I have cut the tabs with the Dremel tool on the sides of the lid where the handles are.

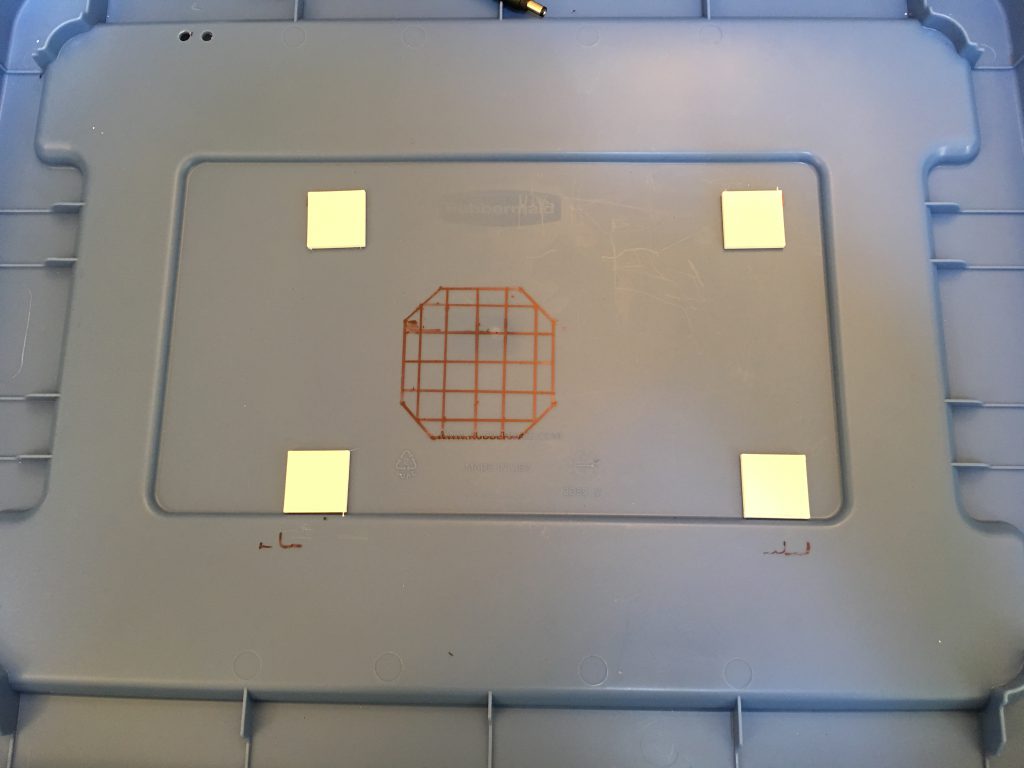
The printer also needs fresh air to cool the control board inside. The Monprice Select Mini has openings at the bottom, so I have cut holes into and elevated the lid with custom legs to provide the air it needs. I used a sheet of paper to copy the exact location of the opening to the lid. The lines are 15 mm apart, and I used an 8 mm bit to drill the holes.
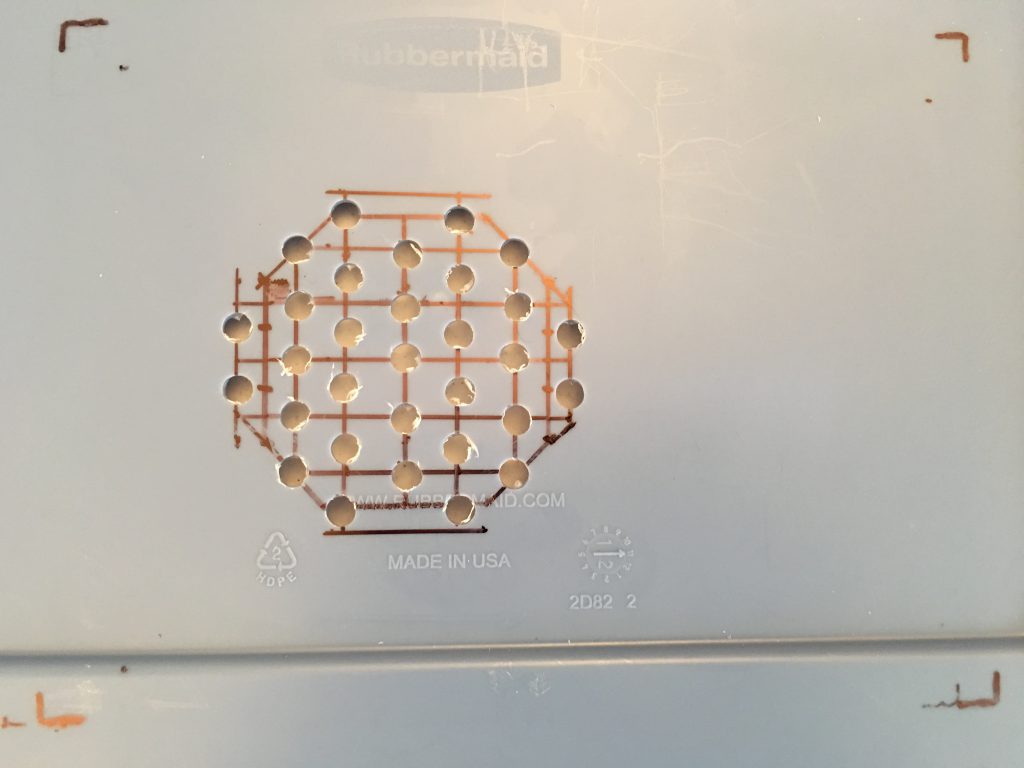


I cut strips of the insulator to lift the printer because I had to pull it forward to provide enough room at the back for the platform. The left side of the printer is much heavier, so it needs more support there.
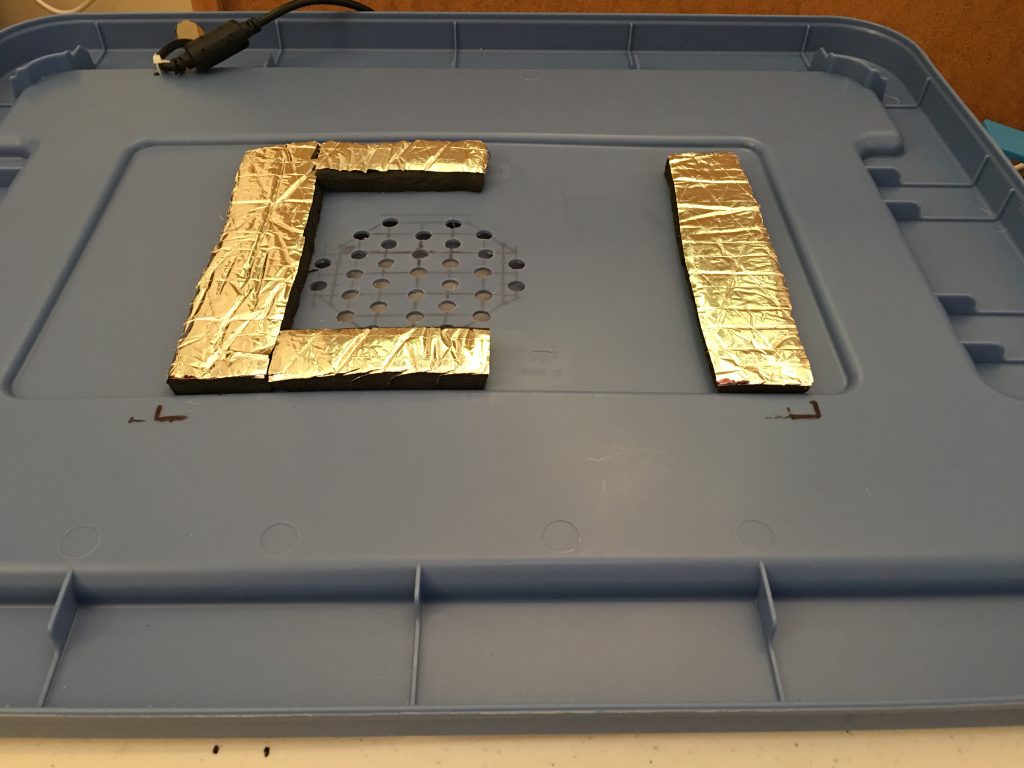
To provide room for the air flow under the lid, I had to print custom legs for the edge and the center to support the weight of the printer. The diameter of the legs is 30 mm. The height at the edges is 5 mm, under the printer 13 mm. I used the flexible TPU material for better noise reduction, and double sided 3M foam tape to secure them.
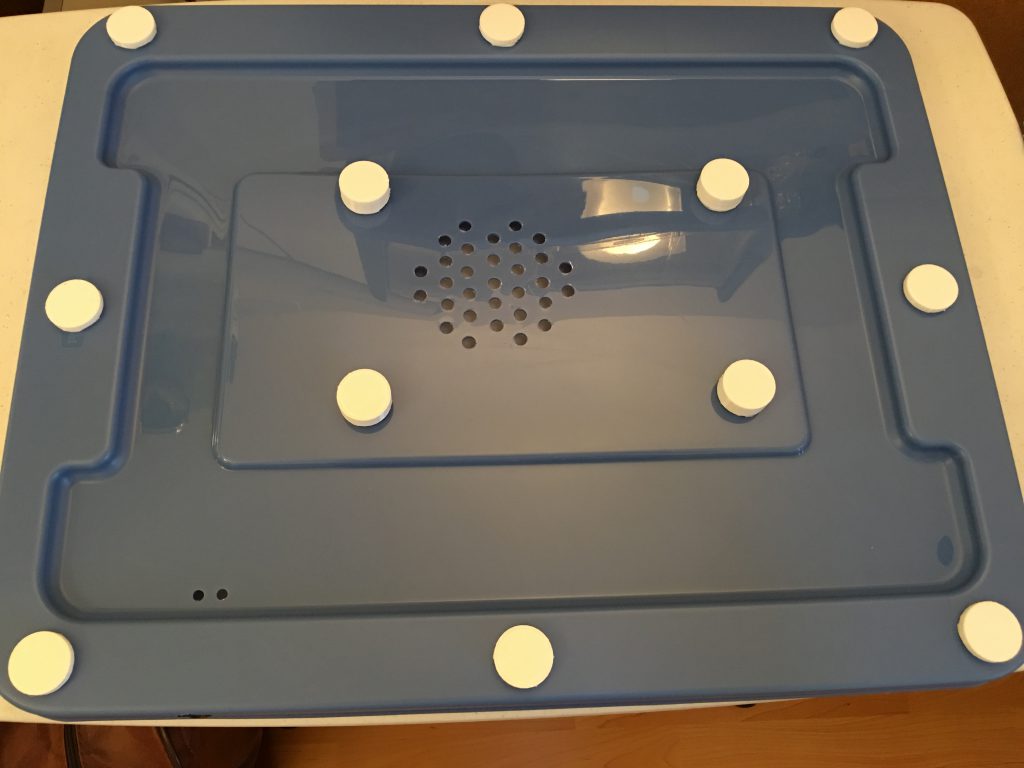


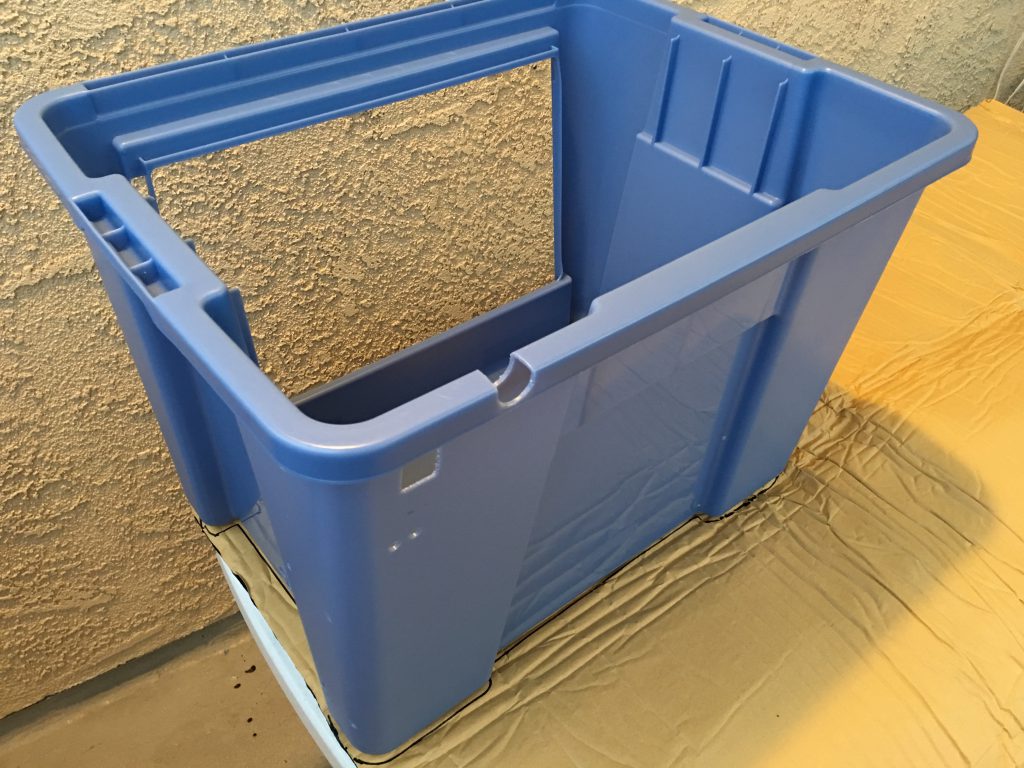
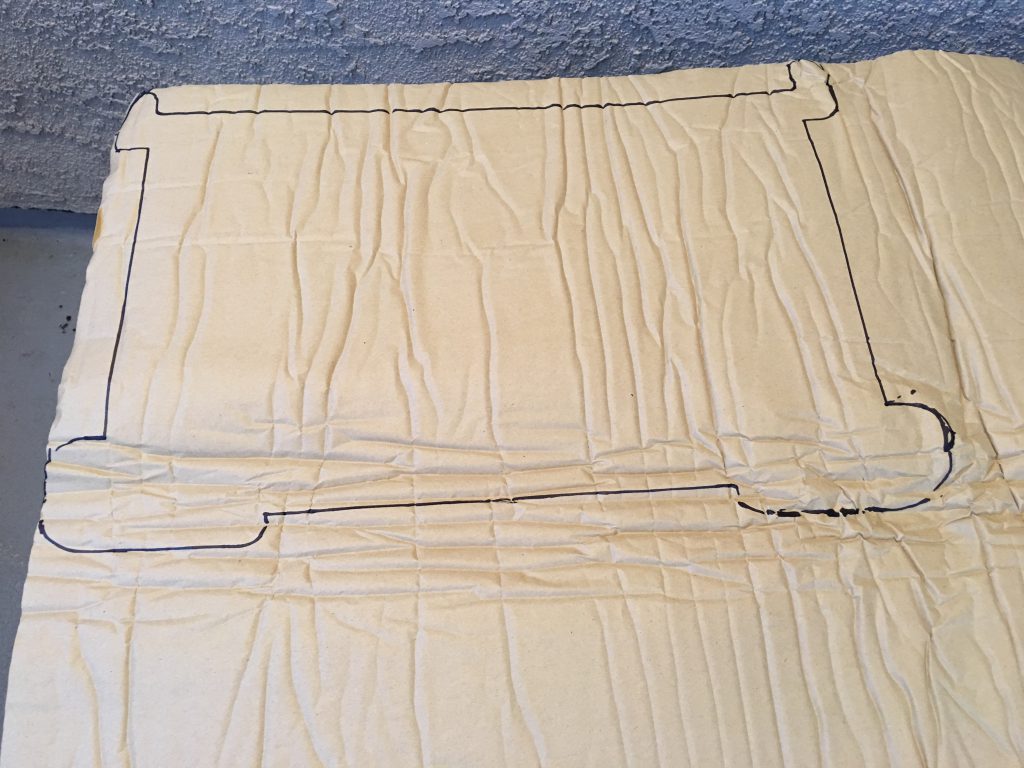
I traced the box to cut the insulator. For the back and side walls make the insulator larger because the turns need extra material. You can cut the excess after you have pasted it in place.


My dome has a 10mm flat edge around, so I used Elmers Glue and transparent packing tape to secure the dome from the inside of the box. The insulator provides the additional support. I put the blower wires under the insulator of the back wall. Cut an opening in the insulator for the speed controller, do not hide it, because it needs air for cooling. Cut into the insulator for the output of the blowers.
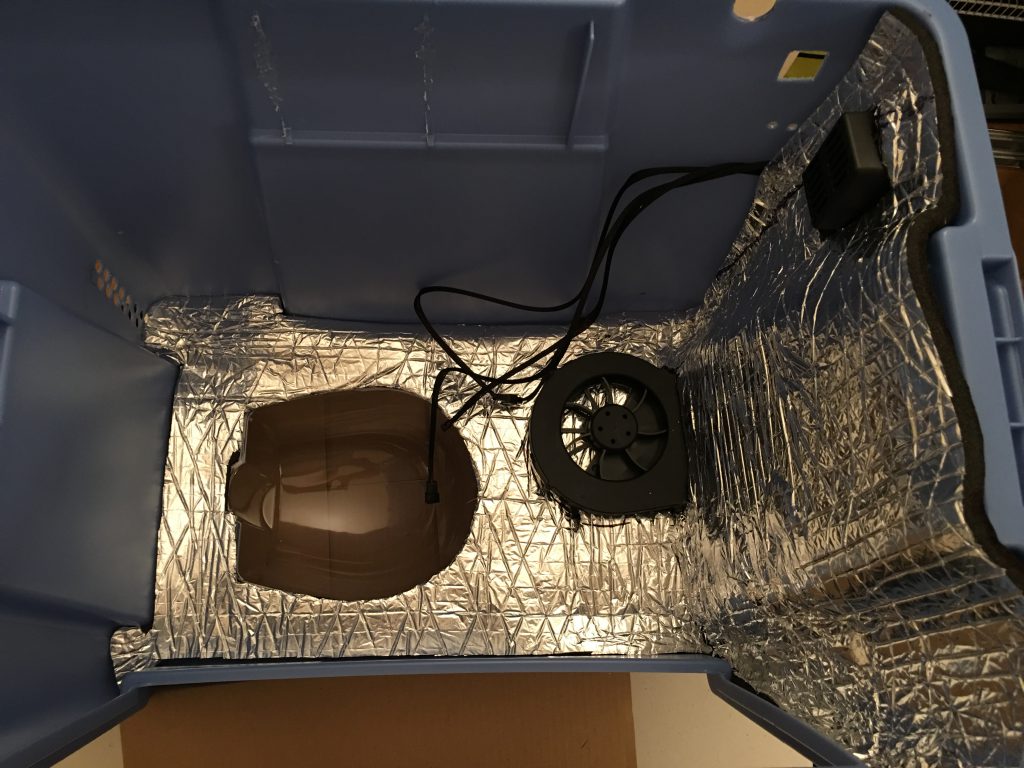

Cut into the insulator where the build platform needs extra room.

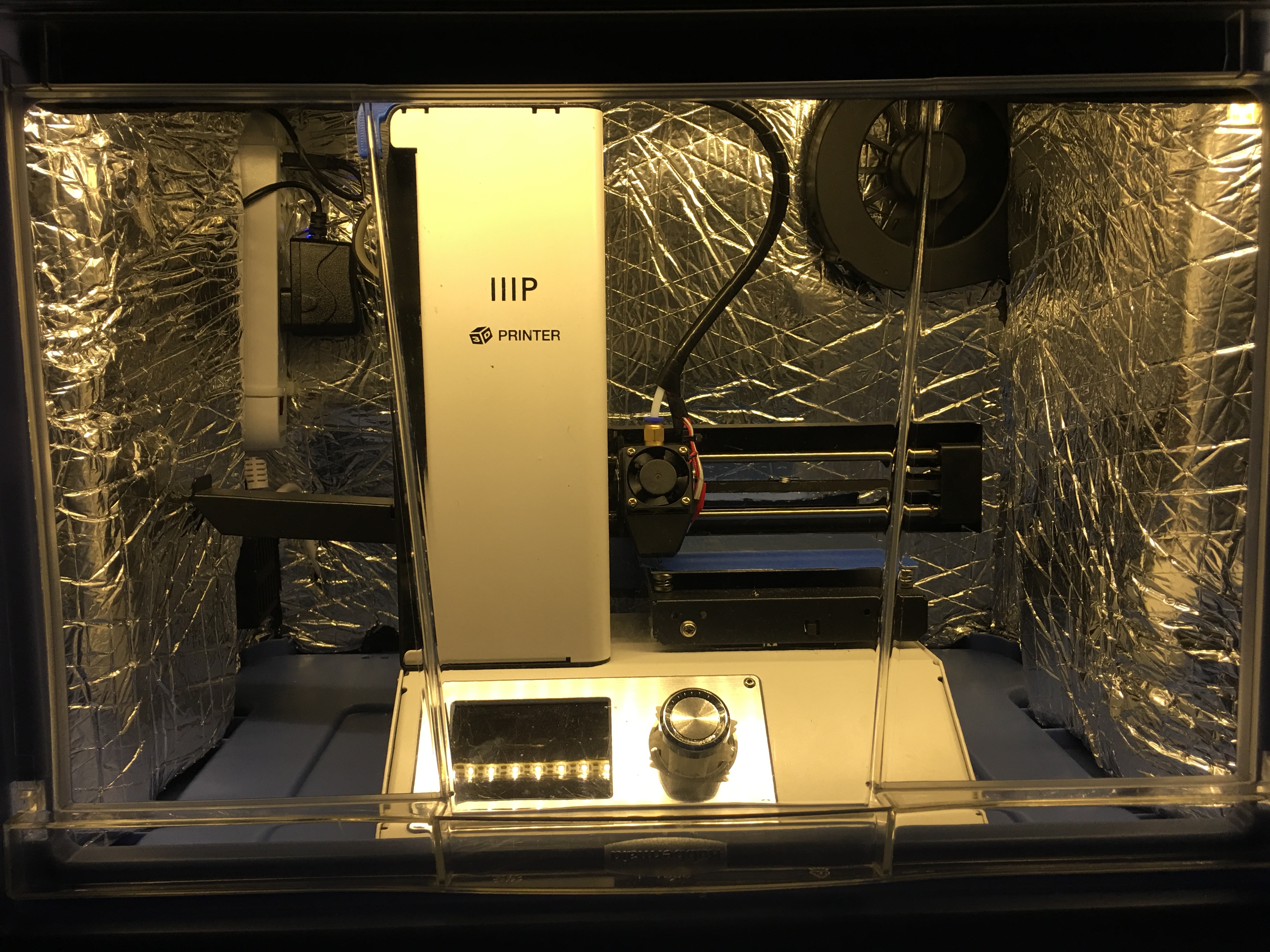
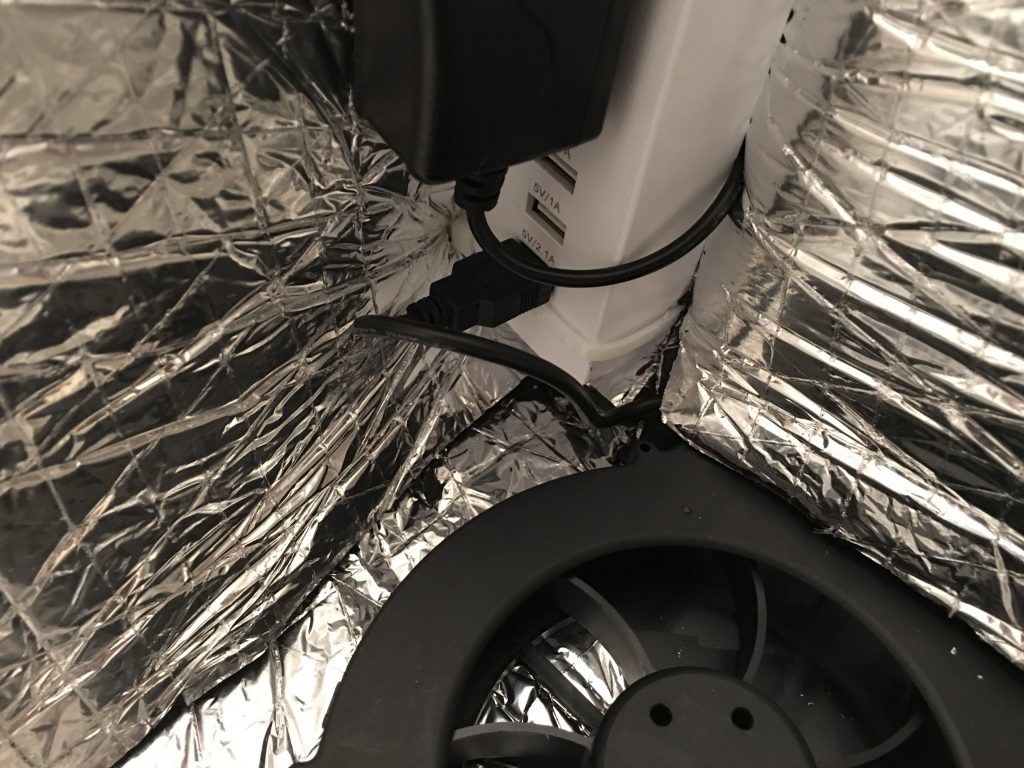
Install the LED strip above the door and hide the wire under the insulator. Use the USB outlets of the power strip to power it.

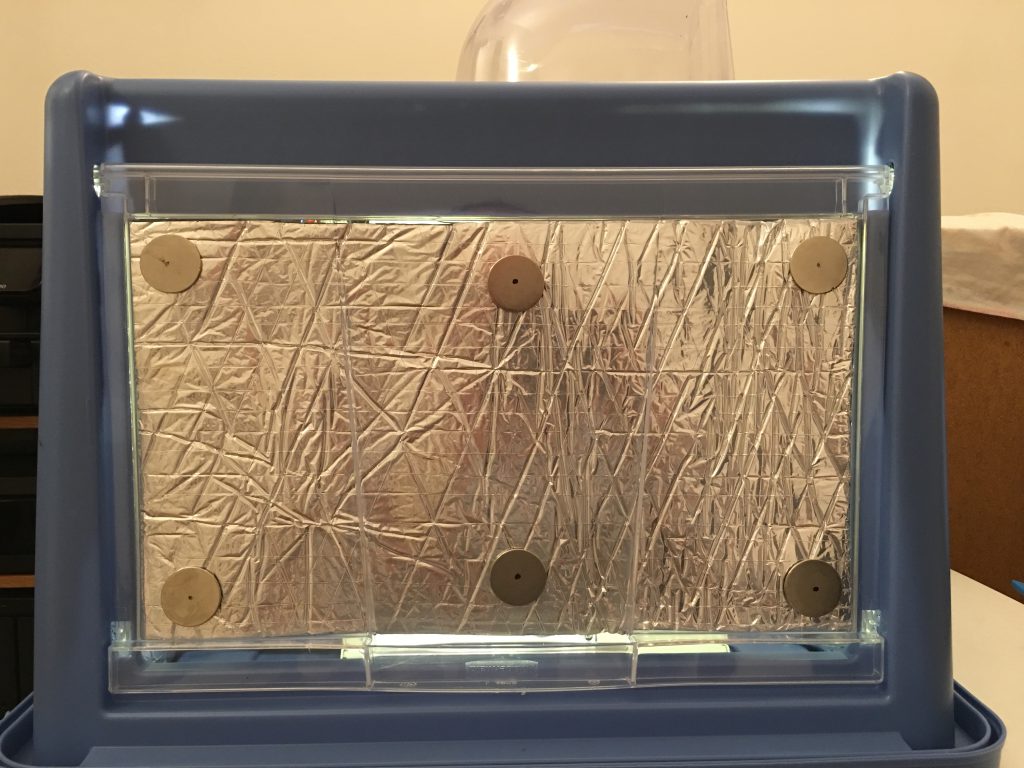
I left the protecting paper on the insulator for the door. I use 12 strong magnets to be able to attach and easily remove the insulator from the door. I hold a magnet on the inside surface of the insulator, and another one on the outside of the door. I could not detect significant noise level differences with our without the door insulator, but during night printing every decibel counts.

If there is a configuration error in the Test Kitchen system, there are commands that can help you to get more information.
Run the instance creation in debug mode
kitchen create -l debug SUITE_NAME
Ruby gems are Ruby programs and libraries with a name, version and the platform that can execute them.
List the installed gems on your system
gem list
Detailed list that includes the author, homepage, license, install location and a short description
gem list -d
Install the latest version of the gem
gem install GEM_NAME
Install a specific version of the Gem
gem install GEM_NAME -v GEM_VERSION
Uninstall the gem from your system
gem uninstall GEM_NAME
Uninstall a gem from a specific location
gem uninstall GEM_NAME -i LOCATION_FROM_GEM_LIST_-D
Update the Gem list in your system after Gem uninstallation
gem update --system
A Chef node is a physical or virtual machine with an operating system that is connected to the Chef server. Once the node has made the connection to the Chef server, the installed Chef Client can execute Chef cookbooks to configure the machine.
Bootstrapping is the process to connect the node the first time to the Chef server, or to attach it again if the node lost the connectivity to the Chef server. To be able to bootstrap a node, your workstation needs to have the Chef Development Kit installed. The kit includes the ‘knife’ command that communicates with the Chef server. Your workstation also has to be able to connect to the Chef server with the YOUR_USERNAME.pem file you store in the .chef directory just above your cookbooks.
Bootstrap a Linux node
To bootstrap a Linux node, open a terminal window on your workstation and execute the command:
With password authentication
-----------------------------
knife bootstrap MY_NODE_IP -x SERVER_ADMIN_USERNAME -P SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD --sudo --node-name THE_NODE_NAME --environment THE_ENVIRONMENT --run-list 'recipe[MY_COOKBOOK1::default],recipe[MY_COOKBOOK2::default]' --json-attributes '{"MY_ATTRIB1":"MY_VALUE1","MY_ATTRIB2":"MY_VALUE2"}'
With key authentication
-----------------------
knife bootstrap MY_NODE_IP -x SERVER_ADMIN_USERNAME -i PATH_TO_KEY_FILE --sudo --node-name THE_NODE_NAME --environment THE_ENVIRONMENT --run-list 'recipe[MY_COOKBOOK1::default],recipe[MY_COOKBOOK2::default]' --json-attributes '{"MY_ATTRIB1":"MY_VALUE1","MY_ATTRIB2":"MY_VALUE2"}'
Bootstrap a Windows node
knife bootstrap windows winrm MY_NODE_IP -x SERVER_ADMIN_USERNAME -P SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD --node-name THE_NODE_NAME --environment THE_ENVIRONMENT --run-list 'recipe[MY_COOKBOOK1::default],recipe[MY_COOKBOOK2::default]' --json-attributes '{"MY_ATTRIB1":"MY_VALUE1","MY_ATTRIB2":"MY_VALUE2"}' -V
where
If the known_hosts file already contains an entry for a different server with the same IP address, we get the error message
ERROR: Net::SSH::HostKeyMismatch: fingerprint … does not match for “…”
Open the ~/.ssh/known_hosts file and delete the line that contains the IP address of the server.
When you need to set a Chef resource attribute based on the current state of the environment, there is a way to dynamically provide the value.
# Set a boolean variable with a test
def MY_BOOLEAN_VARIABLE?
"#{node['domain']}" != ""
end
# Execute a resource and get a reference to it into a variable
t = MY_RESOURCE 'MY_RESOURCE_NAME' do
...
end
# Set the attribute value based on the boolean variable
t.MY_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE MY_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE if MY_BOOLEAN_VARIABLE?