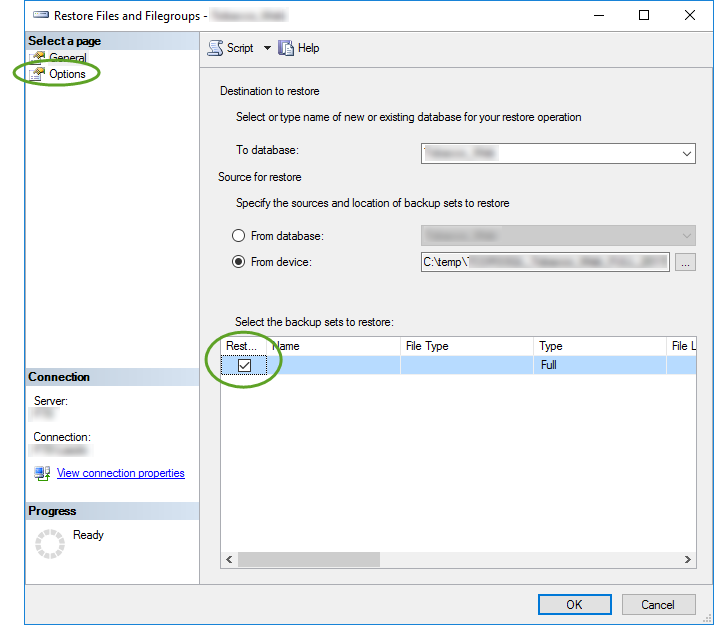
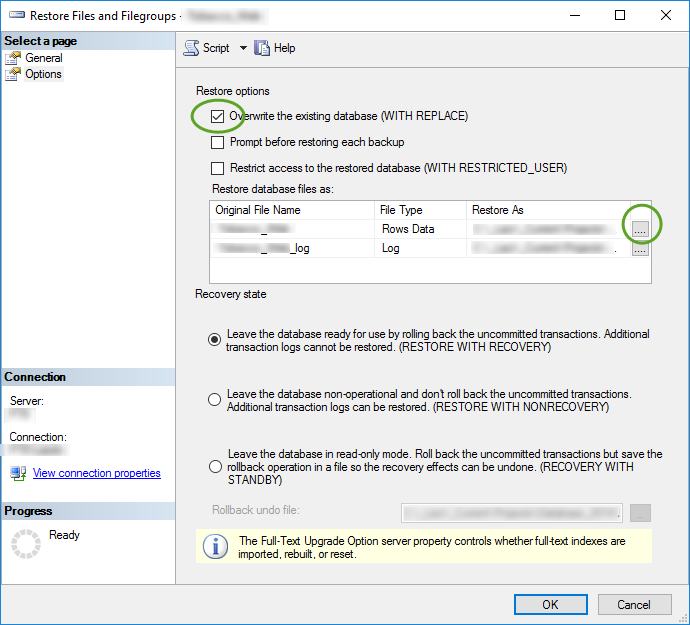
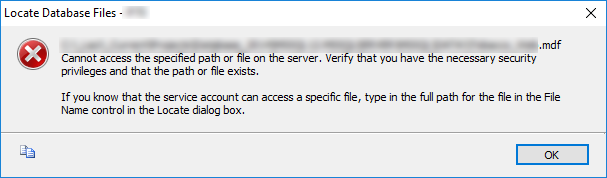
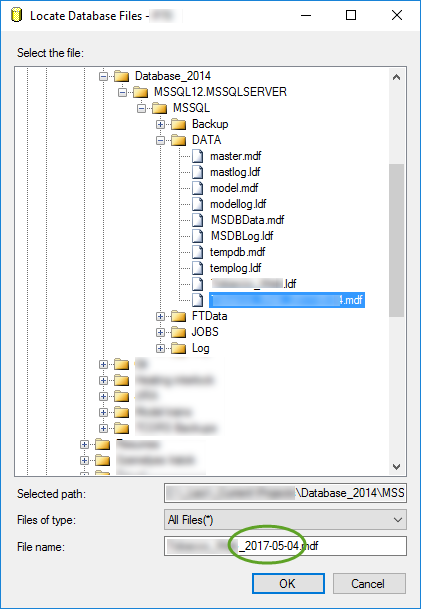
If you work with many Git repositories it is easy to miss a repository when you commit your changes, and very time consuming to pull from all repositories.
It is easy to automate both processes.
In this example, we will place all files in the ~/Git/devops-scripts folder. If you want to place your files at another location change it in the files below.
\/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/
In Windows
To find your home directory on a Windows workstation, open a Bash window (Git Bash) and execute
echo ~
/\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\
Create the Bash script files
- Create a file with the list of Git repositories and save it as ~/Git/devops-scripts/git-repositories.txt
You can separate groups of repositories with empty lines.
# Local_Path+Remote_Path+Rename_the_folder_to(optional)
~/Git/MY_REPO1+https://github.com/MY_REPO1.git+RENAME_TO1
~/Git/MY_REPO2+https://github.com/MY_REPO2.git
~/Git/MY_REPO3+https://github.com/MY_REPO3.git
- Create a file to check the status of all Git repositories and save it as ~/Git/devops-scripts/git-status.sh
#!/bin/bash
# git-status.sh
# Shows the GIT STATUS of the Git repositories and shows the recommended actions
# The list is in git-repositories.txt
eval input="~/Git/devops-scripts/git-repositories.txt" # Need EVAL, otherwise the Bash loop cannot interpret ~ as the home directory if the path contains ~
RED='\033[0;31m'
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
while IFS= read -r folder
do
# Get the length of the path
# On Windows the empty line manifests itself as a 1 character long not empty string
path_length=${#folder}
if [[ ( -n "$folder" ) ]] && [[ ( 1 < $path_length ) ]] ; then
# The path is not empty and the length is greater than 1
# Ignore the lines starting with #
if [[ ! $folder == \#* ]] ; then
# The line is not a comment, process it
# Split the local and remote path
eval local_path=$(echo "$folder" | cut -f1 -d+) # Need EVAL, otherwise the IF statement below does not work if the path contains ~
remote_path=$(echo "$folder" | cut -f2 -d+)
if [ ! -d "$local_path" ]
then
# The local directory doesn't exist.
echo -e "${RED}$local_path does not exist, PULL to get $remote_path${NC}"
else
eval cd $local_path # Need EVAL, otherwise CD does not work if the path contains ~
pwd | tr -d '\n'
status=$(git status)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# To handle
# On branch master
# Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
# Untracked files:
# (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
if [[ $status == *"Untracked files"* ]]; then
echo -e " ---- ${RED}New files added, please ADD${NC}" | tr -d '\n' # -e tells echo to enable backslash escapes
fi
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# To handle
# On branch master
# Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
# Changes not staged for commit:
# (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
# (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
if [[ $status == *"Changes not staged for commit"* ]]; then
echo -e " ---- ${RED}Files changed, please ADD${NC}" | tr -d '\n' # -e tells echo to enable backslash escapes
fi
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# To handle
# On branch master
# Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
# Changes to be committed:
# (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
if [[ $status == *"Changes to be committed"* ]]; then
echo -e " ---- ${RED}Please COMMIT${NC}" | tr -d '\n' # -e tells echo to enable backslash escapes
fi
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# To handle
# On branch master
# Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 1 commit.
# (use "git push" to publish your local commits)
# nothing to commit, working tree clean
if [[ $status == *"git push"* ]]; then
echo -e " ---- ${RED}Please PUSH${NC}" | tr -d '\n' # -e tells echo to enable backslash escapes
fi
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# To handle
# On branch master
# Your branch and 'origin/master' have diverged,
# and have 1 and 1 different commits each, respectively.
# (use "git pull" to merge the remote branch into yours)
# nothing to commit, working tree clean
if [[ $status == *"git pull"* ]]; then
echo -e " ---- ${RED}Repos diverged, PULL to merge${NC}" | tr -d '\n' # -e tells echo to enable backslash escapes
fi
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
echo
fi
fi
fi
done < "$input"
- Create a file to pull from all Git repositories and save it as ~/Git/devops-scripts/git-pull.sh
#!/bin/bash
# git-pull.sh
# Pulls Git repositories and clones the missing ones
# The list is in git-repositories.txt
eval input="~/Git/devops-scripts/git-repositories.txt" # Need EVAL, otherwise the Bash loop cannot interpret ~ as the home directory if the path contains ~
RED='\033[0;31m'
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
while IFS= read -r folder
do
# Get the length of the path
# On Windows the empty line manifests itself as a 1 character long not empty string
path_length=${#folder}
if [[ ( -n "$folder" ) ]] && [[ ( 1 < $path_length ) ]] ; then
# The path is not empty and the length is greater than 1
# Ignore the lines starting with #
if [[ ! $folder == \#* ]] ; then
# The line is not a comment, process it
# Split the local and remote path
eval local_path=$(echo "$folder" | cut -f1 -d+) # Need EVAL, otherwise the IF statement below does not work if the path contains ~
remote_path=$(echo "$folder" | cut -f2 -d+)
rename_folder_to=$(echo "$folder" | cut -f3 -d+)
# Check if the local path exists
if [ ! -d "$local_path" ]; then
# The local directory doesn't exist.
echo
echo -e "${RED}$local_path does not exist, cloning $remote_path${NC}"
# Get the parent directory name
parent_dir="${local_path%/*}"
# Create the parent directory
mkdir -p $parent_dir
# Go to the parent_dir
cd $parent_dir
# Clone the Git repository
git clone $remote_path
if [[ ( -n "$rename_folder_to" ) ]] ; then
# Rename the folder if necessary
end_of_url="${remote_path##*/}"
filename="${end_of_url%.*}"
echo -e "${RED}Renaming $filename to $rename_folder_to${NC}"
mv $filename $rename_folder_to
fi
else
echo
eval cd $local_path # Need EVAL, otherwise CD does not work if the path contains ~
pwd
git pull
fi
fi
fi
done < "$input"
Enable the script execution
\/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/
In Mac OS
- Open a terminal window in the ~/Git/devops-scripts folder
- Run these commands to enable the execution of the Bash files
chmod u+x git-status.sh
chmod u+x git-pull.sh
/\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\
Create an alias
Aliases allow you to execute commands from any folder in the command line and hide the complexity of the entire command.
\/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/
In Mac OS
If you use the iTerm terminal window
iTerm reads the configuration settings from the~/.zshrc file. If you use iTerm add the alias definitions to the end of the ~/.zshrc file.
- Open the~/.zshrc file and add the lines below to the end of it
If you use the built-in OSX Terminal
The built-in Terminal windows reads the configuration settings from the~/.bash_profile file.
- Open the ~/.bash_profile file and add the lines below to it
In Windows
If you use Git Bash
/\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\
alias status='~/Git/devops-scripts/git-status.sh'
alias pull='~/Git/devops-scripts/git-pull.sh'
Refresh the settings in the Bash shell environment
\/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/ \/
In MacOS
source ~/.bash_profile
In Windows
Close the Bash window and open it again
/\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\ /\
How to use it
Open a terminal window in any folder
To check if you need to add, commit or push files in a Git repository:
status
If you have added new files to the repository you get:
/Users/YOUR_USER_NAME/Git/devops-scripts —- New files added, please ADD
If you have changed files in a Git repository you get:
/Users/YOUR_USER_NAME/Git/devops-scripts —- Files changed, please ADD
If you have already executed the git add . command, but have not yet committed the changes:
/Users/YOUR_USER_NAME/Git/devops-scripts—- Please COMMIT
If you have already committed the changes, but have not pushed the to the remote repository:
/Users/YOUR_USER_NAME/Git/devops-scripts —- Please PUSH
To pull from every Git repository before you start to work and clone the missing ones
pull